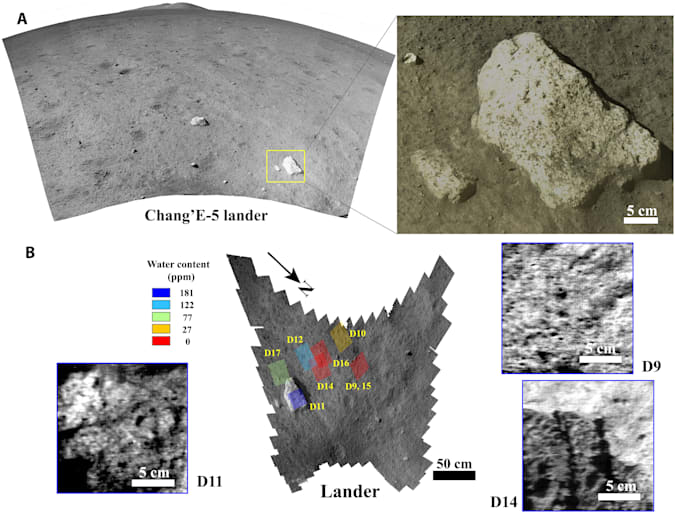
The Chinese lunar lander “Chang’e-5”, as it became known just yesterday, discovered water on the surface of the Moon, which in turn became the first case in history when scientists discovered material and really irrefutable evidence of the presence of this substance on the Earth’s satellite. And if you go into details, then within the framework of a study published in the authoritative scientific journal Science Advances, Chinese researchers argue that the aforementioned lander was able to detect signs of water molecules or hydroxyl, a close chemical relative of H2O.
For this landing module “Chang’e-5” used a spectrometer. It was with its help that the analysis of the regolith composition in the immediate vicinity of the landing site was carried out. It was also found that most of the soil has a water concentration of less than 120 parts per million, which further proves that the surface of the moon is much drier than the surface of the earth. Also, attention should be paid to the fact that Chinese scientists believe that the vast majority of molecules got to the moon as a result of a process called solar wind implantation.
The charged solar particles carried hydrogen atoms to the lunar surface, where they later combined with oxygen, eventually forming water, or hydroxyl. This study, published in the aforementioned journal, is based on NASA findings published in 2018. It was then, if you are not aware, that the above-named agency discovered evidence of the presence of water on the sunlit surfaces of the moon, and this was done using an on-board infrared telescope. For many decades, scientists believed that the Moon was completely and completely dry due to the fact that there was almost no atmosphere on it. Without an atmosphere, as it was believed before, there is not and cannot be anything that could protect water molecules from hard solar radiation. However, the new discovery, although not completely, casts doubt on this theory.