Nowadays the most frequent RAM memory capacity in any type of PC is 8 GB, although it is true that 16 GB are more and more frequent and more in equipment oriented to gaming. But what if you suddenly realize that the operating system is not detecting all that available memory? Let’s see what to do about it.
Let’s start with the obvious: check the software
First of all, one of the first things you should do is enter the PC’s BIOS and make sure that the computer is detecting all the installed RAM, since otherwise you should go to the next point since the problem has to do with with the hardware. In any case, it is always good to first make sure that the installed memory is compatible with your motherboard and that you have the Updated BIOS.
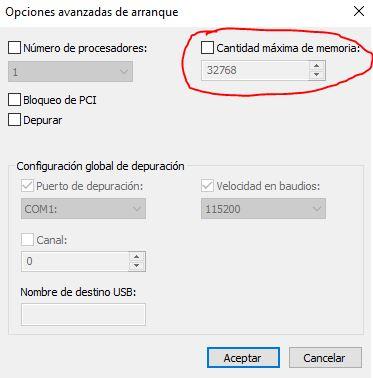
Another thing that you should check at the software level, and especially if you have found the problem with the Windows operating system, is that you do not have limited use of RAM memory by the operating system. To do this, press the key combination WIN + R and type «msconfig»And then press OK; A window called “System Configuration” will open, in which you must go to the second tab, called Startup.
Once here, click on the Advanced Options button … and look at the right part, where it says «Maximum amount of memory», that the box is not checked. If for example the box was checked and the value that appears is 4096 but you have 8 GB of RAM, then the system will work as if you only had 4 GB installed. Whatever you have, ideally this box should be completely unchecked here.
If you had this checked and you have unchecked it, click OK, then OK again to close the system configuration tool and restart the computer to check if you are now using the full amount of RAM or if the problem persists.
Is the RAM memory working well on the PC?
When the PC is not detecting the full amount of RAM you have installed, it is possible that one of the memory modules (or the socket on the motherboard) has failed. You can easily recognize this problem if, for example, you have 8 GB of RAM in two modules of 4 GB each and the PC only detects 4 GB installed, since this would mean that it is not detecting one of them. You can make sure of this by entering the BIOS and seeing if it is detecting the memory in all the sockets in which it is installed (and if not, in the BIOS you will see which of the modules is the one that is working, so by discarding you will already know which one is the one that does not).
In the event that there is a memory module that is not working, check that it is installed correctly and that it is not physically damaged. Try swapping the position of the memory modules (put the one that doesn’t work where the one that does and vice versa is installed), or try using the other two memory sockets on the motherboard if you have them. Remember that for memory to work in dual channel you must use alternate memory sockets, that is, each module is separated by an empty socket.
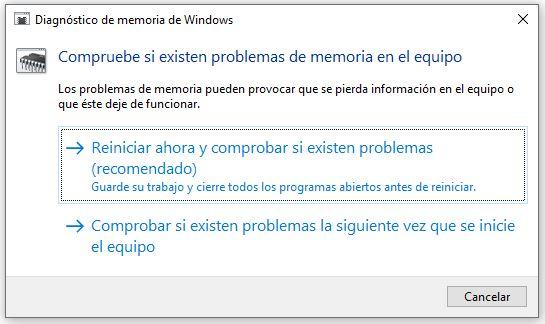
You would also recommend checking if any of the modules are broken by running the integrated Windows 10 diagnostic tool. To do this, click on the Start button and type “Windows memory diagnostic” to open the application and, when you do, it will open a window that will ask you if you want to restart the computer now to check for problems or if you want to schedule its execution the next time you turn on the PC.
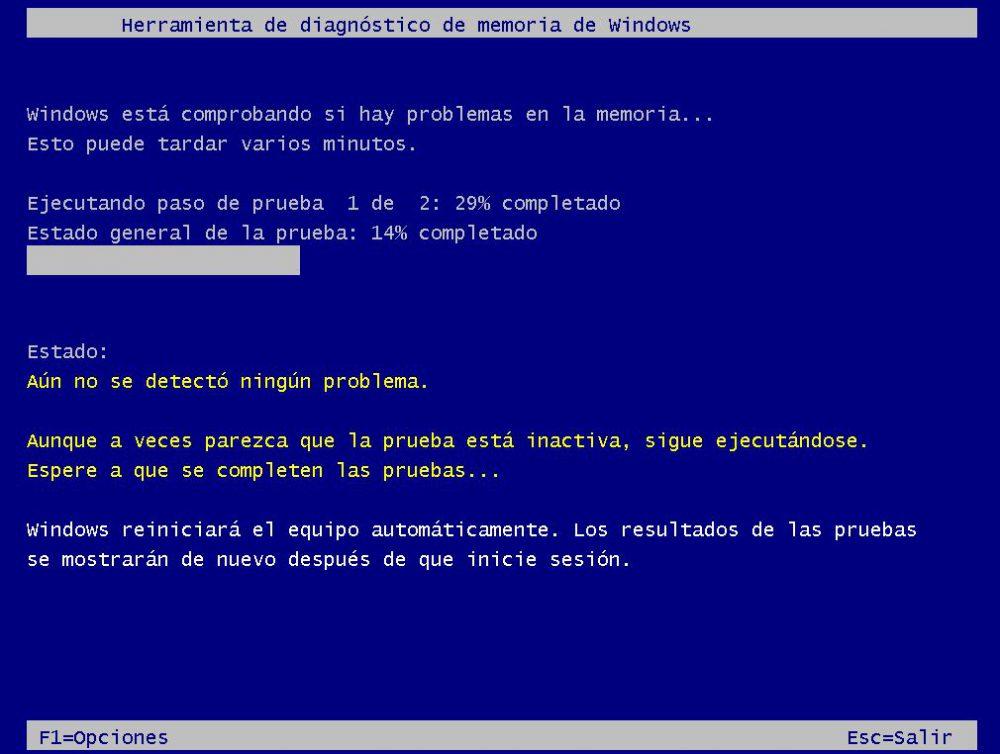
When the program runs, the system will start up with a blue screen that will allow you to select what type of test you want to perform, and you will be able to choose between the Basic test (faster but less exhaustive), Standard (a middle ground, the recommended option) or Extended (takes a long time but performs a thorough RAM check).
Once you choose the desired option, the system will check if the RAM is working well or if, on the contrary, problems are found. Just let it do its job and wait patiently for it to finish (when it does it will automatically restart the PC).
If an error is found, the system will show it when you start the operating system again, and then you will know that one of the RAM memory modules is bad and that is why the PC does not recognize it correctly. In any case, you will know that you have to buy new RAM because the one you have does not work well.
Be careful with the integrated graphics
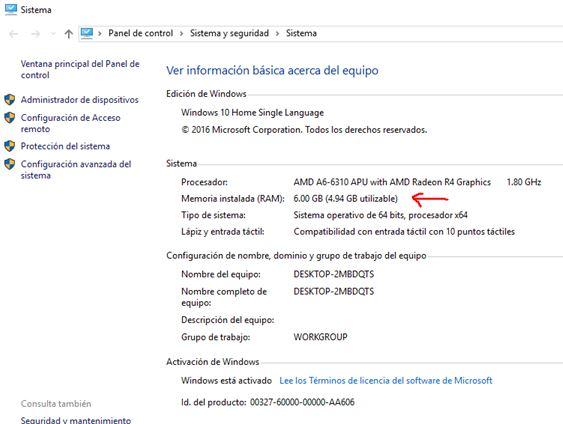
Integrated graphics cards use part of the operating system’s RAM memory as dedicated video memory, and if you don’t have a dedicated graphics card, it’s something you’ll have to live with because the iGPU needs a certain amount of reserved memory. In this case, the operating system will detect the total capacity of your RAM but it will tell you that only a certain part is usable.
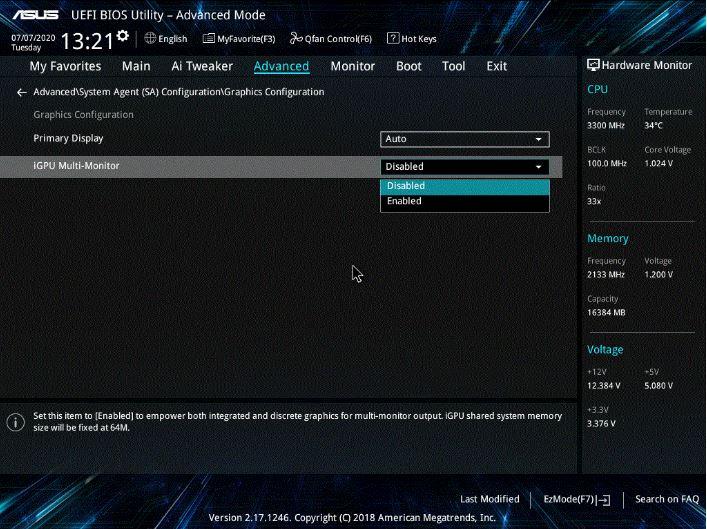
The amount of RAM reserved for the integrated graphics can be configured in the BIOS, as well as you can configure if you want to disable it, which in fact is what you would have to do in case you have a dedicated graphics. As a general rule, the system detects when you have a dedicated graphic and deactivates the iGPU automatically, so it will not have RAM reserved for it, but there are times when this does not happen and you will have to manually deactivate it so that it stops consuming memory.
After disabling the iGPU, save the changes and reboot the system; if the problem was that, you will have recovered the lost RAM memory capacity.