DLSS 3 is an evolution of the well-known rescaling and reconstruction technology supported by artificial intelligence from NVIDIA, which maintains that base but introduces, at the same time, a very important innovation that has allowed it to make a significant leap in performance without depending on other components: frame generation.
The DLSS 3 technology has two parts, one that is the process of rescaling and intelligent reconstruction of the image, which was already present in DLSS 2, and another that is the generation of frames by artificial intelligence. The latter is the one that represents that important innovation to which we have referred, and we are going to delve into it in this article.
However, we are not going to limit ourselves to talking about the generation of frames. So that you can better understand what DLSS 3 is, how it works and what value it brings We are going to review its two parts in depth. However, if after reading this article you have any questions, you can leave them in the comments and we will help you solve them. Without further ado, let’s get down to business.
NVIDIA DLSS 3: Image Reconstruction and Rescaling
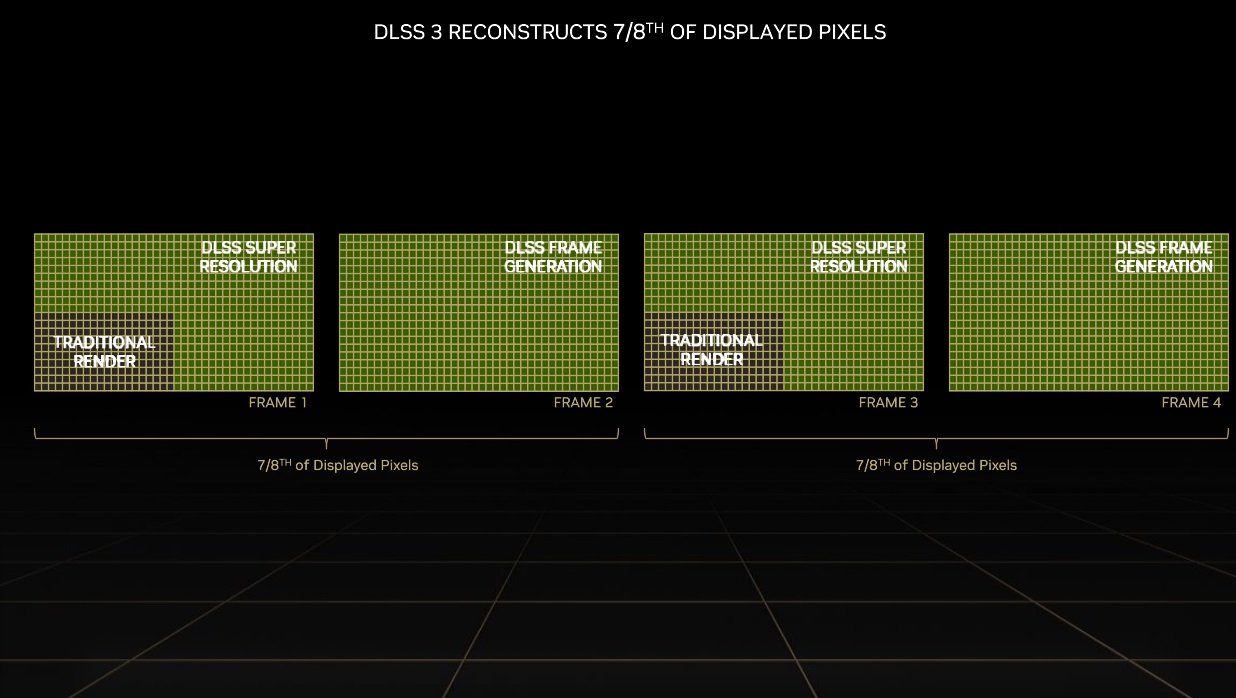
DLSS 3 technology maintains, as we have said, the image reconstruction and rescaling process. Thanks to artificial intelligence, the algorithms used by this technology can create frames with a high final resolution and high image quality, starting from images rendered with a lower number of pixels to the target resolution.
The process is very easy to understand with an example. When we use DLSS 3 in performance mode and we have a target resolution of 3,840 x 2,160 pixels, the rendering resolution becomes 1,920 x 1,080 pixels. algorithms combine previous frames with the current frameand they resort to spatial and temporal elements, and also to movement vectors, to create a high-quality frame that will maintain excellent detail in both near and far objects, and even those with low geometric loading.
Traditional upscaling systems do not use artificial intelligenceand they don’t resort to temporary elements either, they simply they are limited to padding pixels starting from a spatial base that, in the simplest cases, is equivalent to “stretching pixels”. Other more advanced ones use fixed algorithms that slightly improve the result, but do not reach the level that we would obtain with DLSS 3, since they tend to show a much lower definition and lower level of detail, which in the end translates into a blurred and lackluster appearance. They are also prone to flickering problems and the disappearance of distant objects, especially when they have a low geometric load.
Thanks to the image reconstruction and rescaling process offered by DLSS 3, which is also present in DLSS 2, it is possible to create a frame with a quality very close to native 4K starting from a 1080p resolution. This implies a significant performance improvement, and minimal sacrifice in terms of image quality. However, lowering the resolution increases the graphics card’s reliance on the CPU, making it unfeasible to lower the resolution to levels where the processor may end up creating a bottleneck.
Frame generation: the solution to the CPU bottleneck
When DLSS 3 was presented from NVIDIA, they confirmed that the most important novelty introduced by this technology was the frame generationnoting that this would work in conjunction with image reconstruction and rescaling to further improve performance.
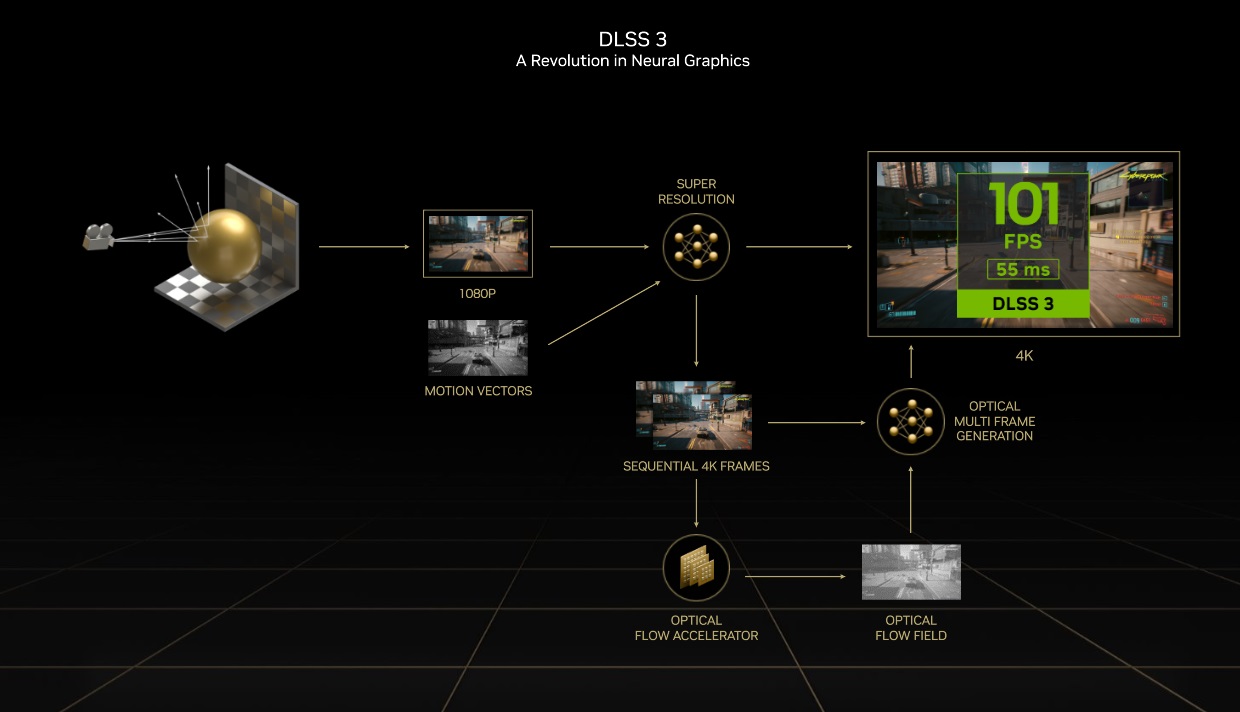
The process of rescaling and reconstruction of the image using artificial intelligence takes place in the tensor nucleiwhile the frame generation runs on the “Optical Flow Accelerator”a component found on the GeForce RTX 20, GeForce RTX 30, and GeForce RTX 40 graphics cards.
This graphics engine speed up the entire workload which involves the generation of frames, and works together with AI DLSS Frame Generationwhich is the one that decides how all the information obtained during the frame generation process is used, and the one that defines the final result.
Frame generation is intended to improve performance, but it does not resort to a resolution reduction, and it is not an optimization of the reconstruction and rescaling process. This technology analyzes two sequential frames that have been rendered in the traditional way, that is, with the intervention of the CPU, and uses the information from those frames and previous ones to generate an additional frame totally independent, that is, without the intervention of the CPU. the cpu.
We might think that DLSS 3 “invents” a frame, but this would be a mistake, because what it really does is generate an additional frame with the information it obtains from other frames, and it uses artificial intelligence, motion vectors and optical flow (“Optical Flow”) to get an exact prediction of what all the objects and elements within that frame should look like, including things so complicated with shading and lighting.
With this technology we have one extra frame for every two traditionally generated frames. Said frame is not affected by the CPU, since it is totally independent as we have commented, and thanks to the use of movement vectors, optical flow and intelligent frame analysis, DLSS 3 manages to maintain a very good image quality.
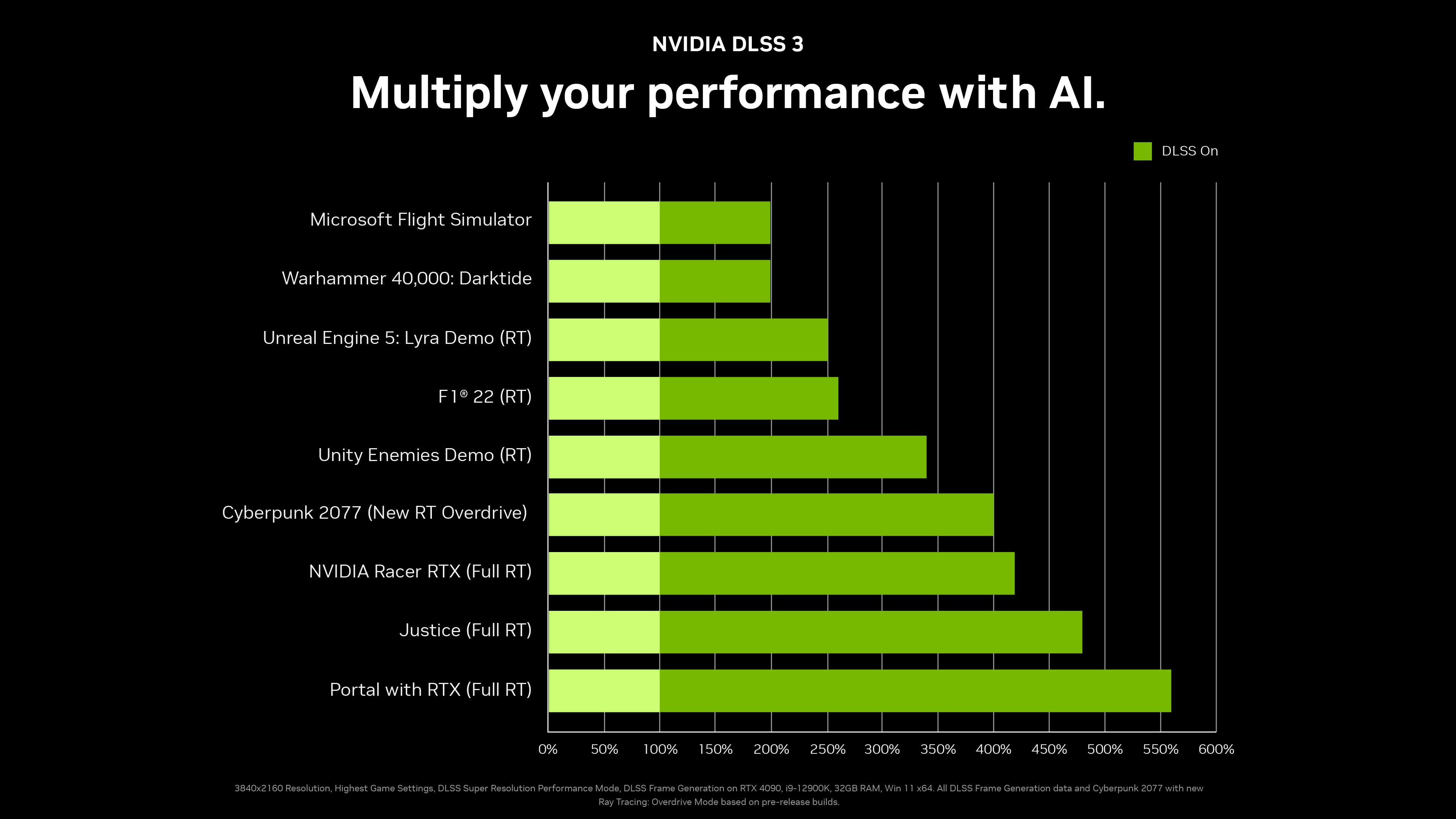
The performance improvement that we can achieve with frame generation is so great that, depending on the game, this can increase by 548% performance vs. native mode. For comparative purposes, the improvement that we would achieve only with DLSS 2 in that same scenario would reach 329%.
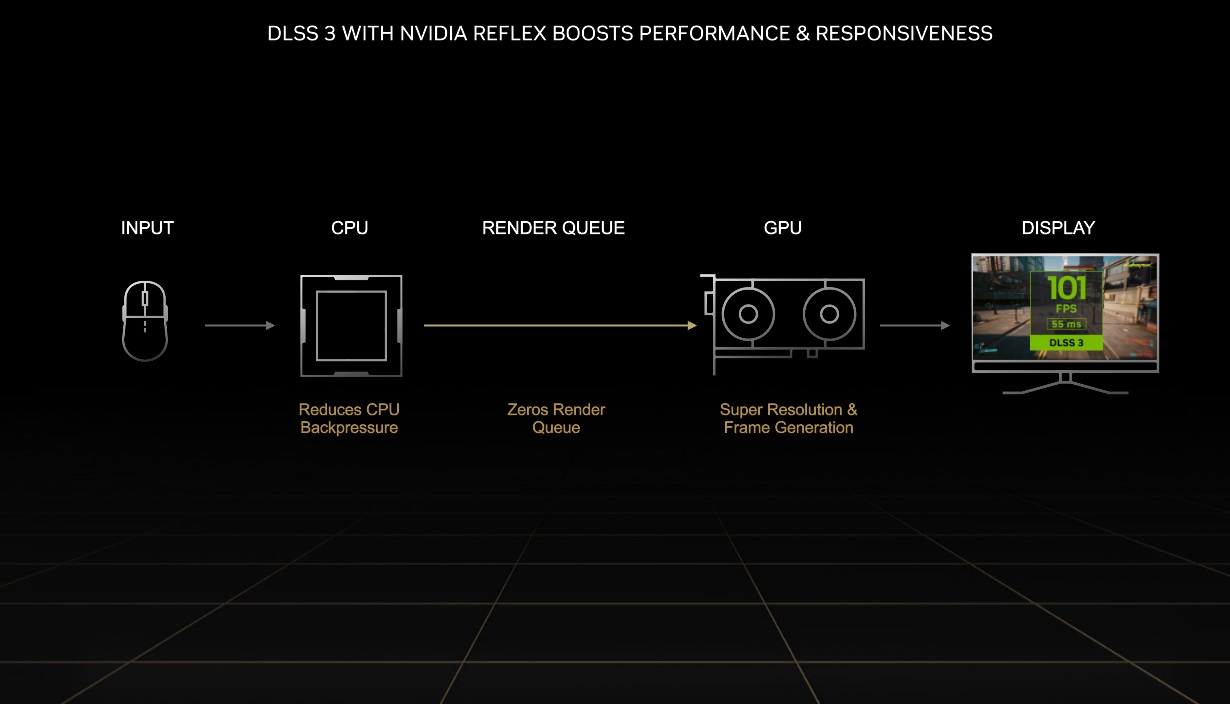
However, the generation of frames has a cost in terms of latency. This could be a problem in specific cases, but NVIDIA has solved it with the reflex technologywhich is automatically activated when it detects that framing is working, and performs a synchronization job between the CPU and the GPU which manages to reduce latency considerably, and makes the response rate in games good enough to enjoy an optimal experience.
DLSS 3 compatible graphics cards and supported games

The center frame has been generated using DLSS 3
We have already said that DLSS 3 uses tensor cores and the “Optical Flow Accelerator”, and we know that the generation of frames is executed on top of the latter. The GeForce RTX 20, GeForce RTX 30 and GeForce RTX 40 have tensor cores and also mount an “Optical Flow Accelerator”, but only the latter are supported for frame generation.
This has an explanation, and it is that the “Optical Flow Accelerator” present in the GeForce RTX 20 and GeForce RTX 30 It does not have the calculation power, nor the sufficient precision, as to achieve a good result with the generation of frames. For this reason, NVIDIA has limited DLSS 3 support to GeForce RTX 40. The GeForce RTX 20 and GeForce RTX 30 support DLSS 2, and NVIDIA Reflex.
Everybody games that support DLSS 3 are compatible with DLSS 2, but not the other way around, frame generation technology needs to be implemented. At the moment, the list of titles that already include support for this technology is very small, but we know that it will gradually expand, as happened at the time with the second generation DLSS.
It should also be noted that, in order to enable DLSS 3 and frame generation in games, these must use DirectX 12since this technology does not work under DirectX 11. It is not a problem, since DirectX 11 is an obsolete and deprecated API, but it is important to be clear about it because, in games that allow us to choose between one and the other, we have to choose the first one in order to activate the generation of frames.