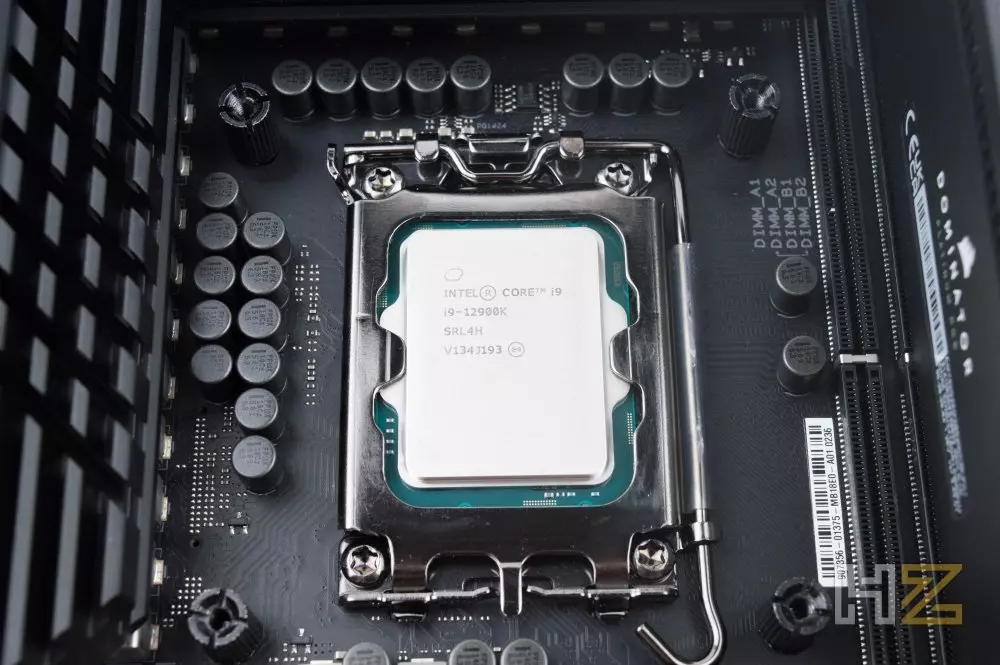
Number of cores
Undoubtedly this is the most important, since the more cores, the more performance. But beware, as the count and naming of cores in Intel processors has changed quite a bit.
The 11th Gen Intel Core (Rocket Lake) and earlier, have only one type of nuclei. From the 12th Generation (Alder Lake), two types of cores have been introduced: P-Cores and E-Cores. If you don’t know what these cores are, don’t worry, here we explain it to you:
- P-Cores: Are the power cores [de ahí el nombre P(erformance)-Cores] And they are always marked. The number of P-Cores will be equal to or greater than the number of E-Cores. Also, P-Cores are the only cores that have processing threads (HyperThreading). These cores are only activated when there is a high workload, such as when we launch a game.
- E-cores: Are the efficiency cores [de ahí el nombre E(fficient)-Cores] And they are always marked. The number of E-Cores will always be less than the number of P-Cores. This type of nuclei lack of processing threads (HyperThreading). They are the cores that are always operational for light loads, such as browsing, working or watching a movie / series. When the P-Cores are activated, they can do the support functions, in order to get additional performance.
Until the 11th Generation processors, it was pretty straightforward. Desktop Rocket Lake generation processors are simple, Core i9s have 12 cores, Core i7s have 8 cores, Core i5s have 6 cores, and Core i3s have 4 cores. But with the new Alder Lakes, things get quite complicated, since for the same range we can have several kernel distributions.
Peculiarities of the Alder Lake
We are going to try to explain a little the particularity of this family of processors, although we must always review the specifications. If we have doubts, by putting the name of the processor in Google, we will go directly to Intel Ark. There it will tell us all the characteristics of the processor, including the number of cores. The specifications of the Intel desktop processors for the range are as follows:
- Core i9: They all have 8 P-Cores and 8 E-Cores
- Core i7: They all have 8 P-Cores and 4 E-Cores
- Core i5: Here begins the dance. The i5-12600K and 12600KF have 6 P-Cores and 4 E-Cores, while the rest of the Core i5s have a 6 P-Cores and 0 E-Cores configuration.
- Core i3: They all have 4 P-Cores and 0 E-Cores
This in regard to desktop processors, in laptops there is much more core dancing, depending on whether the processors are for “normal” laptops or for gaming systems. To resolve any doubts, we recommend searching for the processor model on Google and reading the characteristics of Intel Ark.
Processing threads or HyperThreading
Also called virtual cores, they allow improve processor performance. Approximately, it is estimated that they improve the performance of the processor by 30%. Its main function, explained in a simple way, is to manage the processing thing, optimizing what tasks the processor must do first. Therefore, it is better if the processor has HyperThreading.
It should be noted that in Alder Lake processors and later only the P-Cores have HyperThreading, while the E-Cores lack this technology. For 11th Generation and earlier processors, the integration of processing threads is generation dependent. It may be that some processors do not integrate it, so we will have to look for the processor model in Intel Ark to see if it integrates them or not.
Cache
Said parameter depends directly from the number of cores of the processor. The more cores, the larger the amount of L3 cache.
The cache is used to store data that the processor may need on a recurring or high priority basis. Accessing the cache for the processor takes much less time than accessing RAM, so the more cache the better.
Frequencies
Although it may not seem like it, frequency is very important, especially for video games. The higher the working frequency, the better performance we will get in games. The problem is that in Intel processors we have different frequencies and we must know what each one tells us. These are:
- Work or base frequency: Intel will always show it and it is the minimum processor frequency when we are using it (the processor has sleep modes that reduce the frequency, but they are only activated when we are not using the computer)
- Turbo Boost Frequency: Here we have two types of values
- Turbo Boost 3.0: This is the commercial frequency in Intel processors. This frequency indicates the maximum speed at which the best of the cores can operate of the processor. For example, if the processor has 8 cores, it will only reach 1 of the cores. We have to say that reaching this frequency depends on the load and the cooling system, as well as the temperature of the processor at all times.
- Turbo Boost: Additionally, the processors have a second Turbo Boost frequency. This frequency is lower than Turbo Boost 3.0 and is the maximum that all nuclei can reach. That the processor reaches this frequency also depends on the load, the heatsink used and the temperature of the processor at all times
For Alder Lake processors things get a bit more complicated. As we have mentioned, these processors have two different types of cores. The e cores they have their own frequency of work and lack technology support turbo boost. On the other hand, P-Cores have their own work frequency and these yes admit the technology turbo boost in its two variants.
Usually Intel, at a commercial level, usually indicates the base frequency of the processor and the maximum frequency it can reach, which would be Turbo Boost 3.0.
integrated graphics
All the intel processors they have a integrated graphics (iGPU) designed to take video and little else. Very recently, the company’s processors have begun to integrate Intel Xe graphics, which are more powerful than their predecessors. These already allow you to play a little, it all depends on the type of game, since Fortnite is not as demanding as Cyberpunk 2077.
Although all Intel processors have an iGPU, not all processors have an iGPU. Processors that have graphics, but it is not available for whatever reason, arrive marked. Any word processor “F” or “KF” in the end, it will tell us that the integrated graphics is not operational.
The power of the graphics varies between the four ranges of processors. Normally the Core i9 and Core i7 usually include the more powerful integrated graphics. The Core i5 usually have a solution a little easier and finally, the Core i3 they usually carry a very simple iGPU to show video and little else, in case we do not want to spend on a dedicated graphic.
PCI Express (PCIe) interface
Something that also varies between the four ranges of processors is the number of PCIe lines and the version. This is something habitual and completely normal, but something in which we must be very attentive. Within the Intel Core Alder Lake (12th Gen) family the approximate distribution is:
- Intel Core i9: Count on 20 PCIe 5.0 lanes direct from the processor
- Intel Core i7: Dispose of 16 PCIe 5.0 lanes and 4 PCIe 4.0 lanes for one M.2 SSD
- Intel Core i5: Dispose of 16 PCIe 5.0 lanes and 4 PCIe 4.0 lanes for one M.2 SSD
- Intel Core i3: Dispose of 16 PCIe 5.0 lanes and 4 PCIe 4.0 lanes for one M.2 SSD
There may be more variation in the number of PCIe connections as the chipset adds more of these lanes. It can also be the case of a processor with a different configuration, all based on Intel criteria.
What do the letters on the processors mean?
The letter that appears after the processor number has a meaning, it gives us a lot of information. It tells us certain features and benefits that said processor has or does not have. The most common and that you should know are:
- Core-K: They are capable of overclocking (any processor that does not include this letter lacks support for increasing the frequency of the processor, in theory)
- Core-KF: They also have overclocking capabilities, but lack integrated graphics
- Core-KS: Intended only for Core i9 “black leg” that allow a Turbo Boost 3.0 frequency slightly higher than that of the Core-K
- Core-F: Processors without integrated graphics
- Without lyrics: The frequency is a little lowered compared to the Core-K to adjust the consumption a little more
- Core-T: They are desktop processors with adjusted consumption. Frequencies are usually cut
- Core-U: These processors are designed for general-purpose laptops
- Core-H: Very powerful processors designed for gaming laptops
- Core-HK: Same as Core-H, with the particularity that they support overclocking
These are the most common, although there are other names. Here we leave you the list of all the letters of the Intel processors.
But which Intel processor should I choose?
Well, there is no easy answer as it depends on your needs and your budget. Let’s try to summarize it roughly:
- Core i9: Aimed at demanding gamers who want to play heavy games like Microsoft Flight Simulator in 4K. They are also ideal for gaming and streaming simultaneously.
- Core i7: Intended for those who primarily want to play and maybe stream while playing typical titles like Minecraft, Rust, and other games popular with streamers
- Core i5: They are the best for gaming, due to their excellent performance and adjusted price
- Core i3: More focused on office automation, studying or teleworking, but they are also perfect for gaming
Within this, the ideal is to choose a processor that does not have the “F” in the name. Either to use it without the need for a dedicated graphic or in case the graphic breaks, continue using the PC. The models with the letter “K” are a very good option, since we can obtain extra performance in the future.
There is no single answer, but now you have all the data and with this, you can choose the best processor according to your needs and budget