It is common that when our hard drive approaches the limit of its capacity we want to clean and save as much space as possible. That is why we need to eliminate as many items that may be expendable. One of these objectives can be Windows elements that we create are not necessary or others that we simply do not know are there for. This may be the case of this strange folder that few users know about its usefulness and presence on our hard drive.
What is System Volume Information
It is a folder automatically created by Windows to save certain system information, as mainly those restore points that we create in our operating system. In addition, we can also find in it information about the directories, the Shadow Copy of the files and information about the shortcuts. In this way, if one fails, it can be recovered without much trouble.
But this folder is not only found on the internal hard drive of our PC, but we can also find it on external drives and USB drives that we connect to our computer, since Windows will create it automatically, even if we delete it.
Another of its peculiarities is that its permissions are configured to restrict access both to other programs and users, including administrators. In this way, it is intended to prevent both users and programs without the appropriate permissions, from having access and manipulating the internal files, interfering with important system functions.
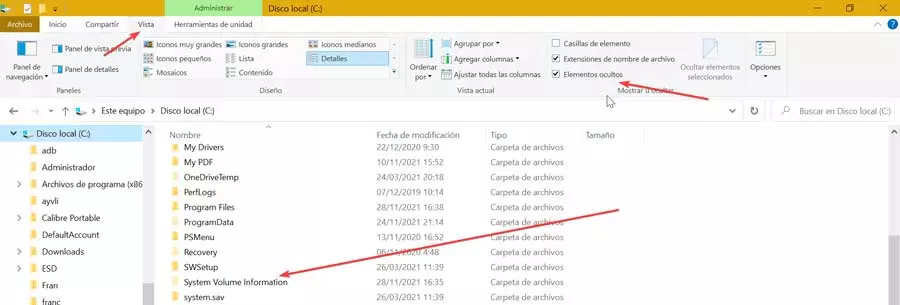
If we enter the File Explorer, click on drive C and take a look at the entire list of folders, we will verify that System Volume Information is not found. However, it is not entirely true, because it really is, but it is hidden.
How to view and access it
To be able to see it, it will be necessary to click on the “View” tab. In the “Show or hide” section, we must mark the “Hidden elements” box. Later we review the list again and verify that it appears. Of course, as we have commented, it is blocked so if we double click to access the following error message will appear: «You cannot access C: / System Volume Information. Access denied.”
And it is that, in general, on NTFS drives like this folder it is locked and can only be used with SYSTEM permissions. Without them we cannot access or delete it. In those units that are formatted in EXT4 or FAT32, it will be possible to access their content. In this way we can even delete them, but it will do little, because Windows will immediately notice and recreate it.
Can I reduce its size?
Normally, in this folder, Windows takes care of store system restore points. The usual thing is that it does not take up too much space on our hard drive. In the event that it occupies more than it should, it is precisely because of the storage of these restore points. That is why, if we want to reduce its size, we must eliminate these points and reduce the space dedicated to them. In this way, its size will be reduced and we will prevent it from growing back more than desired.
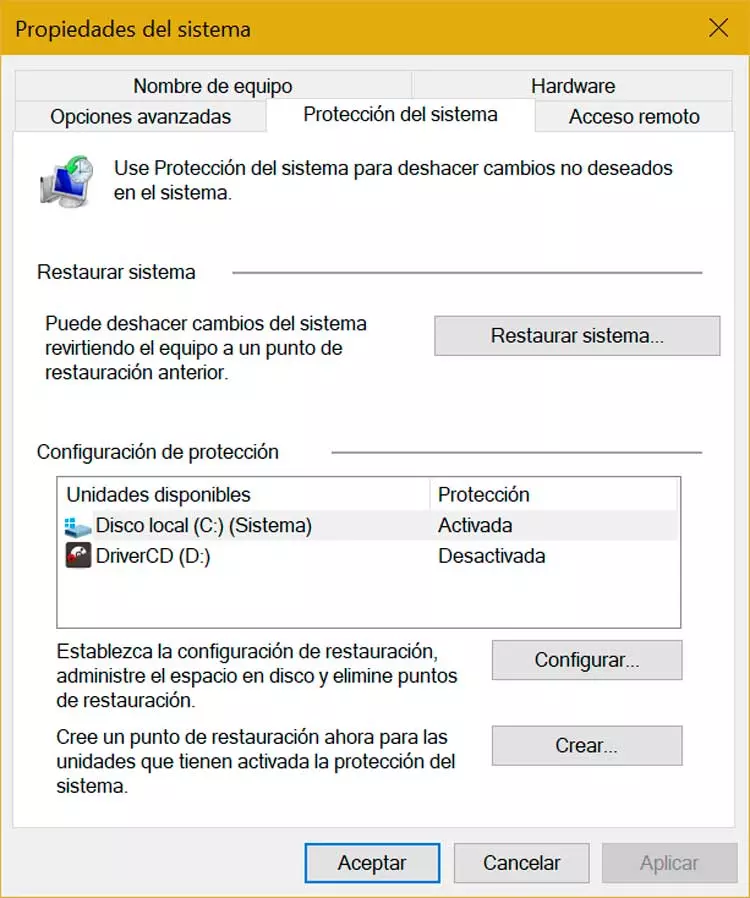
If we are determined to reduce its size we can do it from the Control Panel. To do this, press the keyboard shortcut “Windows + R” and the “Run” command will be launched. Here we write «Control Panel» and press Enter. Later we click on “System and security” and click on “System”. This will open a new window, in which we will click on “System protection”, located on the right side. Again, another window will open.
Next, in the “Protection settings” section, we can choose if “System Restore” is enabled and control how much disk space Windows uses for this task. The mere fact of disabling the System Protection of a unit will not help us to eliminate the System Volume Information folder, since Windows stores more items, but we will be able to reduce part of its size.
What if we delete it?
As we have commented previously, deleting the System Volume Information folder is not an easy task since it will be necessary to have SYSTEM services for it. Also, it is not an action nothing recommendedBecause Windows stores important system data here, so we should not do anything beyond reducing the space allocated for the System Restore utility.
Despite this, if you prefer to ignore our recommendations, in order to access the contents of the folder and even delete its elements, you must assign yourself as the owner of the directory, and grant your account NTFS permissions to be able to access it. This is something we can do from the Security tab itself within the folder properties. However, there is a much faster option to assign yourself as the owner and get direct access. To do this we must do it from the Command Prompt tool.
To access the Command Prompt, we must type cmd in the search box of the Start menu and then click on “Run as administrator”. Once the window appears, we must write the following commands independently, pressing Enter after each one.
takeown /f "C:System Volume information" icacls "C:System Volume Information" /grant woshubjwolf:F
Once this is done from the “Properties” section of the folder, in the “Security” tab, we can verify that the account now has full control permissions. In the case of wanting to restore the original permissions of the System Volume Information folder, we must execute the following commands, also from the Command Prompt window.
icacls "C:System Volume Information" /setowner "NT AuthoritySystem" icacls "C:System Volume Information" /remove woshubjwolf