What is the network configuration when using old routers
If you use old routers to expand the number of Ethernet ports or to improve WiFi coverage, it is absolutely necessary that the configuration at the network level is correct, otherwise you could have connectivity problems due to an IP address conflict, and even both routers “fight” to provide a private IP address through the router’s DHCP server.
The correct configuration of a home network where we have a main router, and one or more old routers, is as follows:
Main router configuration
Depending on the main router you are looking for, you may have the IP 192.168.0.1, 192.168.1.1 and even any other. For example, ASUS routers have an address of 192.168.50.1, manufacturer AVM has a setting of 192.168.178.1.
- Default gateway IP address: 192.168.1.1, subnet mask /24 or 255.255.255.0
- DHCP server: from 192.168.1.100 to 192.168.1.254
This configuration would be the standard in a main router.
old router configuration
The old router must necessarily have an IP address within the range of the main router, therefore, in the previous example we could configure the following IP:
- Default gateway IP address: 192.168.1.2, subnet mask /24 or 255.255.255.0
- DHCP server: disabled.
It is very important that this old router has an IP address that is outside the range of the main router’s DHCP server, otherwise there could be a serious private IP address conflict. In the event that you have more routers connected, they will have to have a unique IP address within the range that we have indicated before, for example, if we have a second old router, it should have an IP address 192.168.1.3 with mask 255.255.255.0, the DHCP server should also be disabled.
How do I know which one I’m connected to?
When we connect to any of the previous routers, either to the main router via cable or WiFi, or to any of the secondary routers, we must bear in mind that we will be able to access all of them through the private IP address that we have configured. For example, if we want to access the main router we will have to indicate 192.168.1.1, however, if we want to access any of the others, we simply have to enter their previously configured IP addresses, 192.168.1.2 and 192.168.1.3 respectively. By not having the DHCP server enabled on the secondary routers, the default gateway will be that of the main router, something essential to have an Internet connection, otherwise, we would not be able to have Internet access, although we could have local access since we are all in the same network segment.
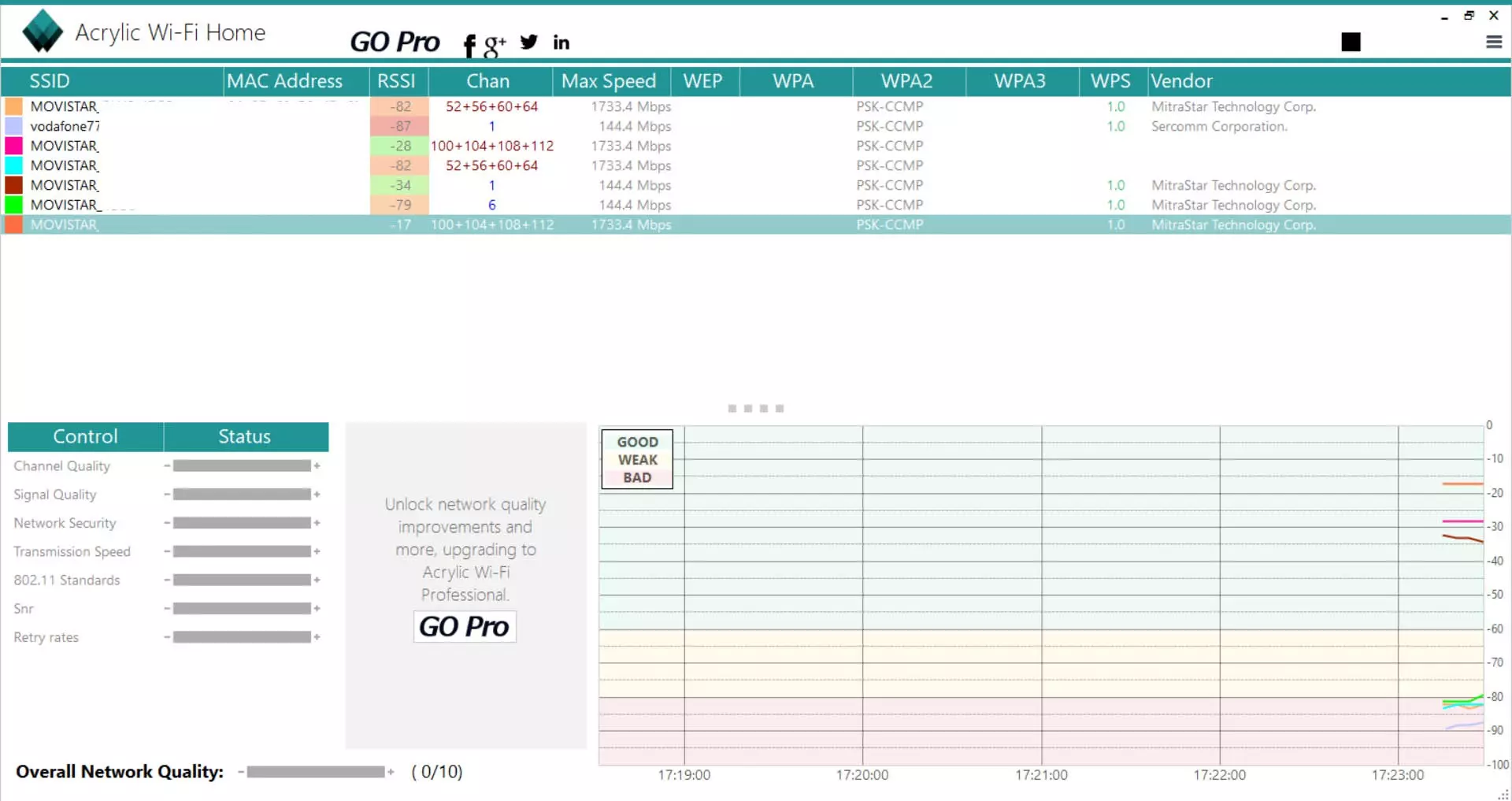
If you want to know which router you are connected to via Wi-Fi (because if you are connected via cable, you will already know which one you have connected to exactly), you will have to look at the MAC address (BSSID) of the specific router, to find out, the easiest way. simple is to download the application Acrylic Wi-Fi Home which is completely free, we open the program and we will be able to see all the Wi-Fi networks that exist, in addition, we will also be able to see exactly what device we are connected to.
With the information of the MAC address, you will have to look at what the WiFi MAC address of your router is, this information is usually in the main configuration menu of the Wi-Fi, or also on the sticker that we have on the bottom of the router with all information about WiFi network name and default WPA2 password. However, you should know that it really does not matter which router you are connected to, because you will have communication in the local network as if you were directly connected to the main router, in addition, the interconnection between the main router and the secondary routers is usually via cable, for what you will have the maximum bandwidth.
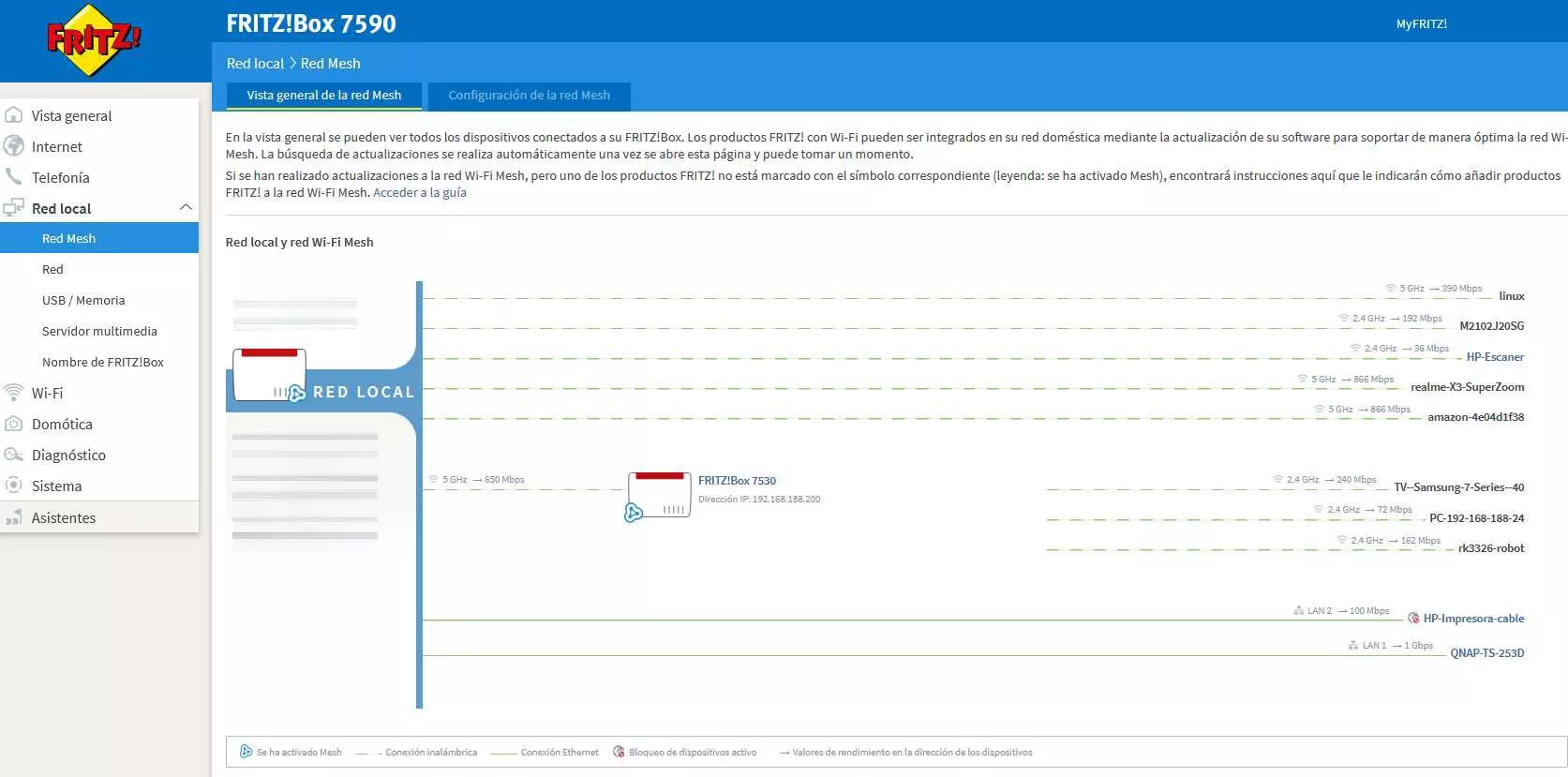
In the case of Wi-Fi Mesh systems, if you want to see which router or node you are connected to, simply access the main router’s administration website and it will tell you which WiFi clients are connected to the different nodes. In a Mesh network, all the devices are integrated and “talk” to each other, so you can always know which WiFi node you are connected to.
As you have seen in the previous screenshot, if you have a Mesh network, the main router will know at all times which node a specific client has connected to.