Therefore, access to bank accounts can be compromised if we are victims of computer attacks of this type. Not only will we have difficulty entering the application or bank account, but we could even lose control and an attacker could impersonate the identity.
Classes of banking viruses
Not all banking virus or malware they act and arrive in the same way. Therefore, we are going to explain what different types there are and how they can compromise our security. There are banking Trojans, fake apps, hidden software, and other methods attackers use to steal information.
Banking Trojans
An example of a banking Trojan is TrickBot. It mainly sneaks in via email via a fake file. What it seeks is to steal financial information from the victim. It can use macros from Excel files, for example, and be able to steal credentials to log into bank accounts.
This type of malware can affect both computers and mobile phones, although in recent years the latter have suffered a wave of attacks with banking Trojans. They are usually designed for a specific operating system, such as Windows or Android, and attack better.
They can enter through a file that reaches us by mail, as in the case of TrickBot, but also when visiting an infected website, due to a vulnerability in the system or when downloading any file from the Internet that contains malicious software and that is going to execute the malware on the computer of the victim.
A banking Trojan will have the ability to capture information, create false redirects and ultimately put a bank account at risk. It can achieve total control and act as if the victim is actually running something.
fake apps
A type of banking malware that also affects both the computer and mobile versions quite a bit are fake apps. Basically, as the name suggests, they are fake programs They pretend to be legitimate. They will try to make the victim believe that what they are installing is their bank’s software, but in reality it is something malicious.
A fake banking app has the same goals as a banking Trojan: stealing information, taking over account control, and impersonating your identity. Sometimes it will even look almost the same as the legitimate application, so the victim may fall for it and leave the data on a tray.
Mainly the attack starts when we put the bank details. That information will travel to a server controlled by the attacker. In this way it can steal the password and take control, acting as if it is really the victim who makes a payment or carries out any action.
hidden software
Something similar happens with hidden software. In this case it is a legitimate, safe program that has some spyware. For example, an attacker can take advantage of some vulnerability in a program to sneak in additional software and that is going to be what really puts security at risk.
With this, when the victim logs in or performs any action with the banking application, the spyware will be collecting data. All this always in a hidden way, without the victim being aware that she is exposing the bank information when logging in or making a payment.
keylogger
A keylogger, although it is not a specific malware for banking accounts and applications, is also going to be a significant problem. In this case we are dealing with a type of software that is responsible for collecting passwords. What it does is record the keystrokes keystrokes made by the user and thus steal the username and password.
It usually arrives through malicious files or fake programs that are installed by the victim. They can be more or less sophisticated, since some focus solely on recording what is written once it detects that a session is going to be started in a service. It is, therefore, another way they can use to compromise security.
bank phishing
In this case, we are not dealing with a specific type of malware, but rather with a strategy. Phishing consists of scam the victim to log in through a fake link. By putting the data, that information will go directly to the hacker and not to the bank servers where we try to log in.
It is a classic in password theft and it also affects bank accounts. For example, something common is that we receive an email indicating that there is a problem with our bank account. We may be asked to log in to change some of the settings, send some data, etc. But of course, we are really entering a false page.
How to be protected
After explaining the types of banking malware that exist and how they can compromise our security, we are going to give some essential tips to be protected. The objective is to avoid intruders in our accounts and that they do not put personal information and bank details at risk.
keep everything up to date
The first thing is to have everything updated. Many types of malware in general, and banking in particular, are going to take advantage of some security flaw. Once they exploit that vulnerability, they will be able to sneak in malicious software without us realizing it and steal passwords or take control.
You should always have the updated operating system, but also any applications you use or network drivers. In all these cases you must have the latest versions and correct any known vulnerability so that it is not the entry point for banking viruses and other threats.
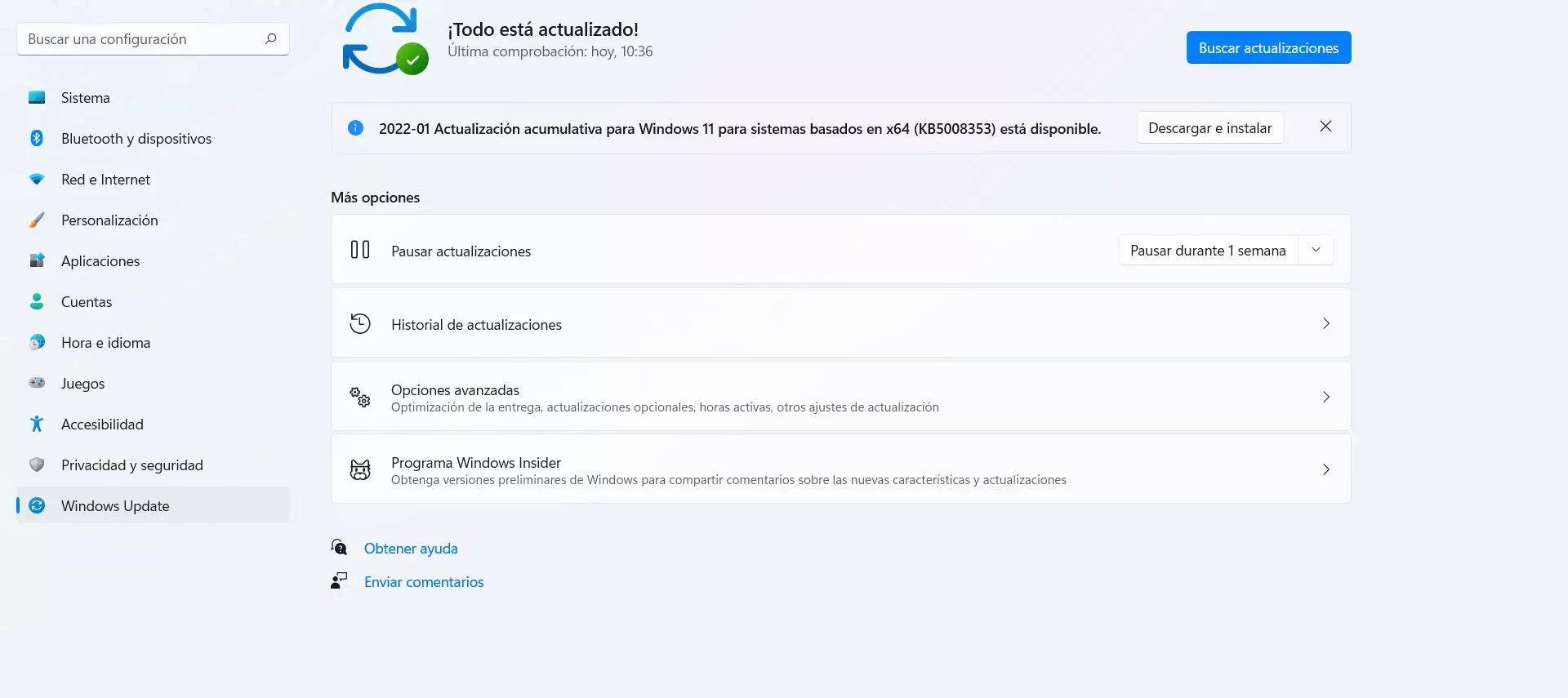
In the case of Windows, to update it you have to go to Start, enter Settings and go to Windows Update. There you will see possible files that you can install and have everything updated correctly. It is something that you should do periodically to always have everything correctly installed.
Use security software
Of course, another very important point is to use security programs. A good antivirus it is essential to prevent the entry of malware and also to detect possible malicious software on your computer and remove it before it can compromise your security and privacy.
For example, Windows Defender is a good option. However, there are many free and paid alternatives. Some like Avast or Bitdefender also come in handy to prevent attacks. However, whichever you choose, you must make sure that it works well and that it is really going to protect you.
Install only official apps
Something fundamental is to use only official programs. This means that you should avoid third-party applications and that you find on sites outside the official pages of the bank or stores such as Google Play. It is true that sometimes you can find applications outside the official ones that have certain additional functions, but that can be a risk.
A hacker could use these alternative programs to sneak in malware. Therefore, our advice is to always download them from safe sources, such as the bank’s website and reliable application stores. This will help to at least reduce the risk that you are installing some kind of fake software.
protect networks
Having your networks protected and using secure wireless networks will also help you avoid banking malware and related attacks. Some attacks will take advantage of insecure connections to get in the way and steal information, passwords and, ultimately, compromise security.
Therefore, whenever you go to log into your bank account you must ensure that you are on a secure network. You should avoid public Wi-Fi networks, such as a library, shopping center or airport. However, if you need to make a payment or log in to these types of networks, you can always use a VPN to encrypt the connection.
Common sense
But if there is something important to avoid banking malware and any type of computer attack in general, it is common sense. Avoid making mistakes It is essential to avoid infecting the system with threats and not falling into the trap of hackers, as is the case with Phishing or by installing fake applications, for example.
Keep in mind that most computer attacks will require us to make a mistake. Therefore, if we do not fall into basic traps such as opening a malicious file that comes to us by e-mail, installing an unofficial program or logging in outside of reliable sites, we will have a lot to gain from being properly protected.
In short, as you have seen, there are different types of banking viruses. It is essential to be protected and know how to identify threats as soon as possible so that passwords and personal data are not compromised at any time.