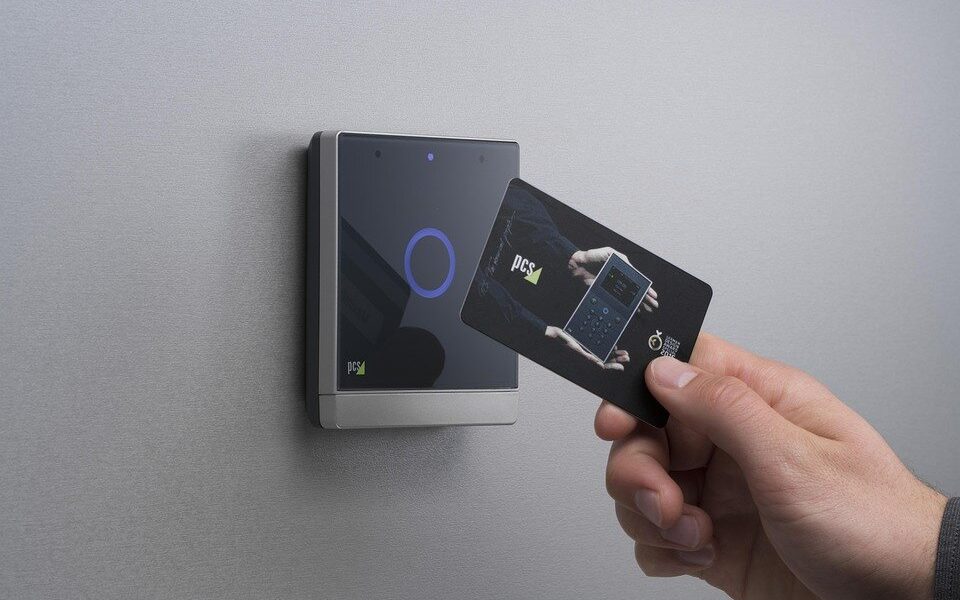
RFID or radio frequency identification is a technology where the data is encoded in intelligent labels or tags. A reader captures the data through radio waves and can read outside the line of sight.
There are a few significant factors to take into consideration before choosing an RFID tag. The tags are known as low frequency (LF), high frequency (HF), and ultra-high frequency (UHF) tags. High Frequency RFID consulting is required to understand behavioural patterns of the frequency. There are various advantages and disadvantages associated with each tag.
Low Frequency
The frequency band lies between 30 and 300 kHz, with wavelengths around 2,400 meters. The low-frequency RFID system can only use a small range between 125 to 134 kHz, and the effective wavelength allows it to penetrate metal and water quickly.
The LF tags are expensive compared to HF and UHF tags; however, the cost depends upon the application. These tags are powered via magnetic coupling, which makes them last indefinitely. The LF tags come in various shapes and sizes, using the same magnetic coupling for power. However, the data rate takes longer for the reader to receive and decode the signal.
Applications
The LF tags can cost anywhere between a hundred to a thousand dollars. They have low-security standards; therefore, they are not recommended for encrypted communication. These tags are primarily applicable for pet and livestock tagging.
High Frequency
The high-frequency spectrum lies between 3 to 30 MHz. The wavelength is shorter than the LF tag – only around 22 meters. A high-frequency tag also uses magnetic coupling and can pass through most materials except water and dense metals.
HF tag is generally used for near-field communication or NFC. The International Standard Organization has approved it, and NFC operates with a single global frequency standard. As NFC is accepted for hundreds of applications, it is mainly inexpensive and easily adaptable. With magnetic coupling, HF tags can last a lifetime unless damaged by wear and tear. NFC tags can also be read through smartphones with HF/NFC readers, which is why they have gained widespread popularity.
Applications
- Marketing applications
- An interactive experience for a brand marketing
- Access control applications
- Data transfer applications.
- Ticketing applications
Various countries also adopt HF tags for their passports. A metal lining addresses users’ privacy to lower the read range along with a secure password of the RFID tag. Due to its widespread application, High Frequency RFID consulting is gaining popularity. One can easily find the applications of HF RFID in data transfer applications as the systems are sensitive to interference.
Ultra-High Frequency
The ultra-high frequency can lie anywhere between the range of 300 MHz to 3 GHz. The protocol standards are put in place by GS1. In addition to that, several countries have their frequency standards when it comes to RFID.
Without these standards, there would be the following repercussions:
- Devices would have interfered with each other’s signals and show poor bandwidth.
- Adoption of advanced technology would be challenging without bands having similar signalling standards.
UHF RFID requires a significant investment when compared to HF and LF. UHF tags are also subdivided into various categories like high temperature and high memory. However, the tags last the lifespan of the applicant, and they are not dependent on a power source.
Applications
- Tool tracking
- IT asset tracking
- Race tracking
- Laundry management
- Oil and gas industries
- Vehicle tracking
- Tracking pipes and construction equipment
Final Thoughts
Consultancy is required to understand the industrial needs of RFID tags before choosing one. The most convenient way of analyzing the requirements is to research the environmental factors and read range, material, and tag size restrictions before going for the best.