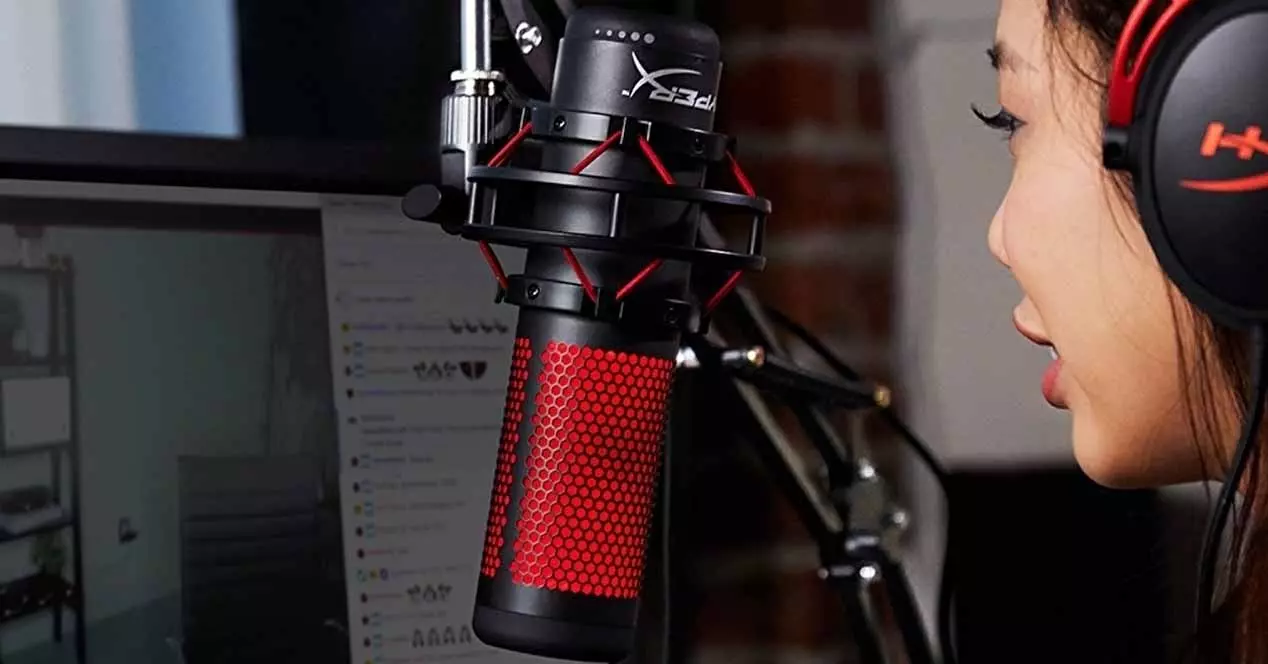
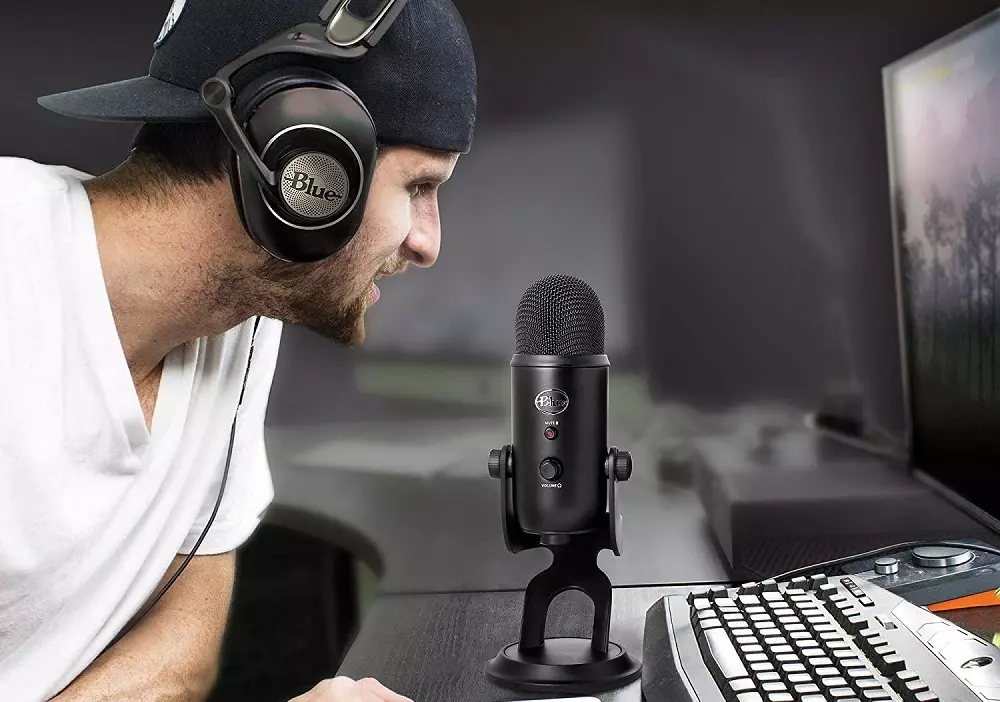
When we have a voice communication over the Internet, the last thing we want is for anything other than our own voice to be heard, but for this to be possible there are a number of factors you should take into account and thus obtain the best possible quality; However, the quality of the transmission and the noise that enters it depends to a large extent on the quality of your microphone, so although miracles cannot be worked you can always find a lot of room for improvement.
How to prevent PC noise from seeping into the microphone
Unless you are a fan of silent computing, all PCs make some noise to a greater or lesser extent, and when we talk about the noise sneaking into the microphone, it could very possibly even have to do with the air that enters and leaves the PC even though you barely hear it, since it looks quite amplified in a microphone. . In any case, just like the noise of the PC, we are not interested in any other type of noise entering the communications, such as that of the cars that pass by the street near your window or the barking of the neighbor’s dog, since as We have mentioned before at the end the primary objective is that our voice is heard and nothing else.
There are quite advanced microphones that integrate noise cancellation systems which are tremendously effective in eliminating background noise, but obviously not everyone has the resources to purchase one of these models; However, there are many things that can be done about it and that is what we are going to see next.
Check your microphone’s recording pattern
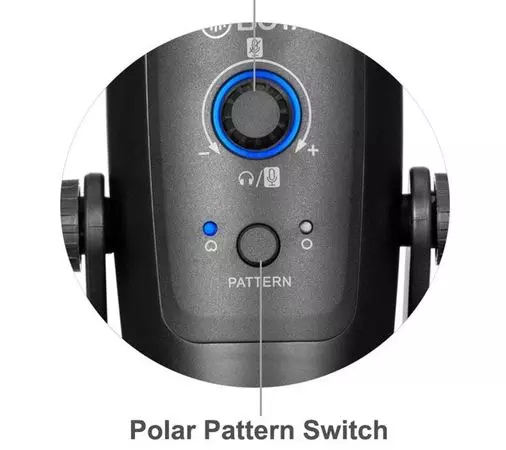
Most tabletop microphones that connect to the PC via USB (at least the ones with a bit of quality and renown) usually have several polar patterns that are selectable from the device itself. In general, most of these devices have a cardioid pattern, but in many you can select up to 4 in total: cardioid, omnidirectional, stereo and bidirectional.
In this regard, you should know that the ideal polar pattern to prevent any type of noise from seeping into the microphone is the unidirectionalAlthough unfortunately we only find it in some microphones integrated in headphones and in other more specialized devices that are rarely designed for PCs. After the unidirectional, whose pickup pattern is as its name indicates in a single direction, we have the cardioid as the second best option and which is also the most widespread among PC microphones, since let’s say that 90% of the sound they pick up is at a 45º angle at the front, while the remaining 10% is at the rear.
In a cardioid microphone some noise from the PC or other things in your environment can sneak in, but it will be quite little, and also you can almost always counteract it to some extent by regulating the gain (we will come to that soon).
Microphone placement is vital to avoid PC noise
If you place the microphone right between where you are sitting and the PC, it will obviously pick up some of the noise it emits even though you have selected the cardioid pattern since, as we have indicated, it also picks up some of the sound that comes from behind. Therefore, the first advice that we are going to give you regarding the placement of the microphone is that you do not put it near any source of noise, such as the PC, the window, etc.
Likewise, it is quite interesting that you consider the possibility of not placing the microphone on the same table where you have the PC, because if it is a desktop microphone it will absorb some of the vibrations produced by the PC itself, by the keyboard when typing or by your hands moving to move the mouse or simply by resting your wrists on the table; his thing is to have an articulated arm (which now we will also talk about that soon) or place the microphone on a piece of furniture that we have next to it, preferably on the opposite side of where the PC is.
Check gain to reduce incoming noise
If, despite having the microphone well placed and with the optimal pattern selected, noise from the PC or other sources continues to creep in, you should check its gain. In many microphones this can be done through controls on the device itself or through its software if the microphone is USB, but regardless of the type, brand and model of microphone you have, you can always control its gain from the Windows sound options.
To access these settings, right-click on the speaker icon in the Start bar (next to the clock) and select “Open sound settings”. In the middle of the window you will see the microphone, and just below the “Device properties” button. Click on that option and a window will open that will show you the same thing that we have put in the capture above these lines, where the “Volume” slider bar is actually the microphone gain.
We recommend you to try to find the right balance between the capture of your voice and the ambient noise, since combining the pattern, a good location and a selection of the gain you will surely be able to cancel or at least mitigate the noise that the PC makes. in your recordings.
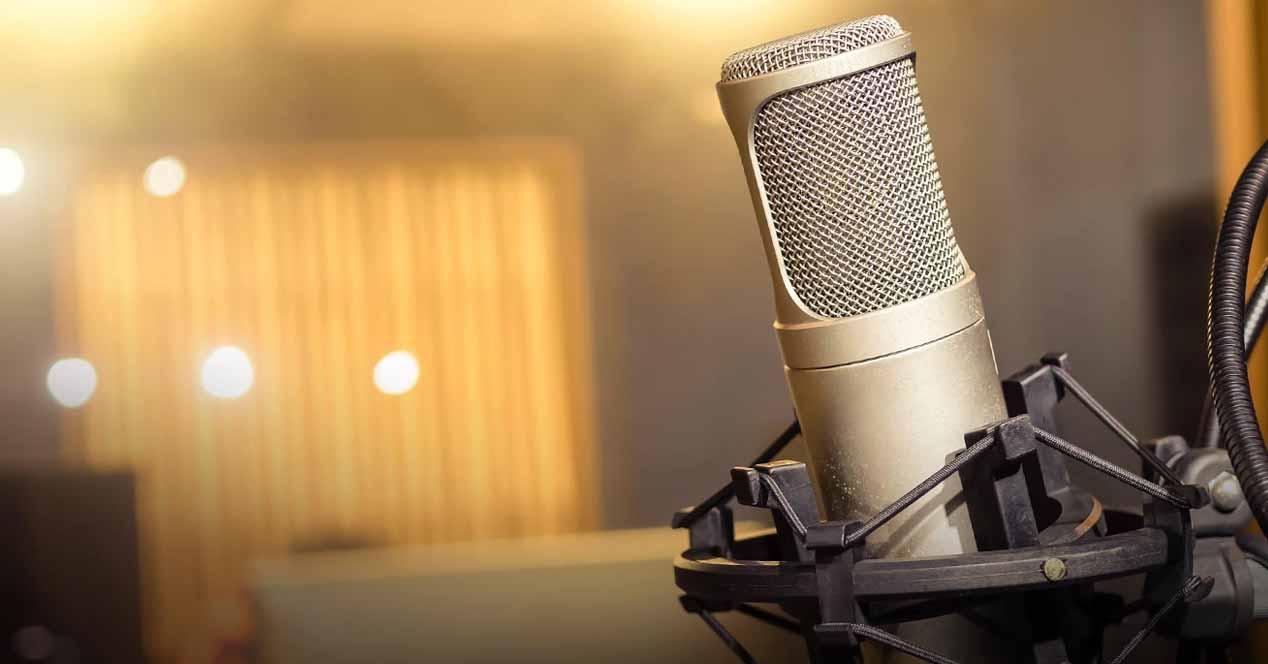
Accessories to reduce noise
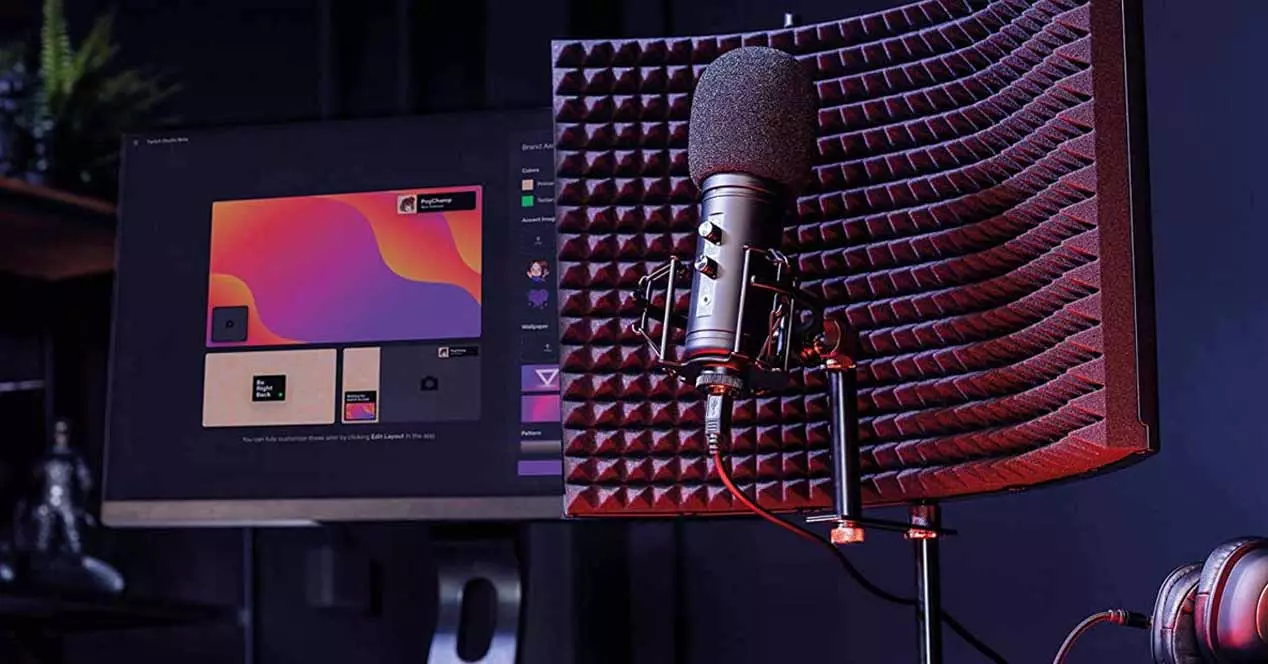
If nothing of what we have told you so far has worked for you, there are also other options to reduce the noise that the microphone picks up, although it is true that these will force you to spend some money. For example, a movable arm will allow you to always place the microphone in the position you want, or a spider support will keep the microphone on edge, thus preventing any type of vibration from sneaking into the recording.
You also have sound-isolating panels that you can put behind the microphone as in the example image that we have put above, thus avoiding any sound that does not reach the microphone from the front; of course, you can also buy the popular pop filter that, while not reducing noise in and of itself, serves to prevent the “pop” noise that we all make when we open our mouths to speak from seeping into the recording.