Last April we saw that AI had a lot of potential in the semiconductor industry. It was NVIDIA that confirmed that this technology was capable of create better chip designs, and that it could do it in less time than a team of up to ten people. There is no doubt that this information was very interesting, and in fact it fit with the statements of other giants in the sector, such as Google for example, but what real implications had it had?
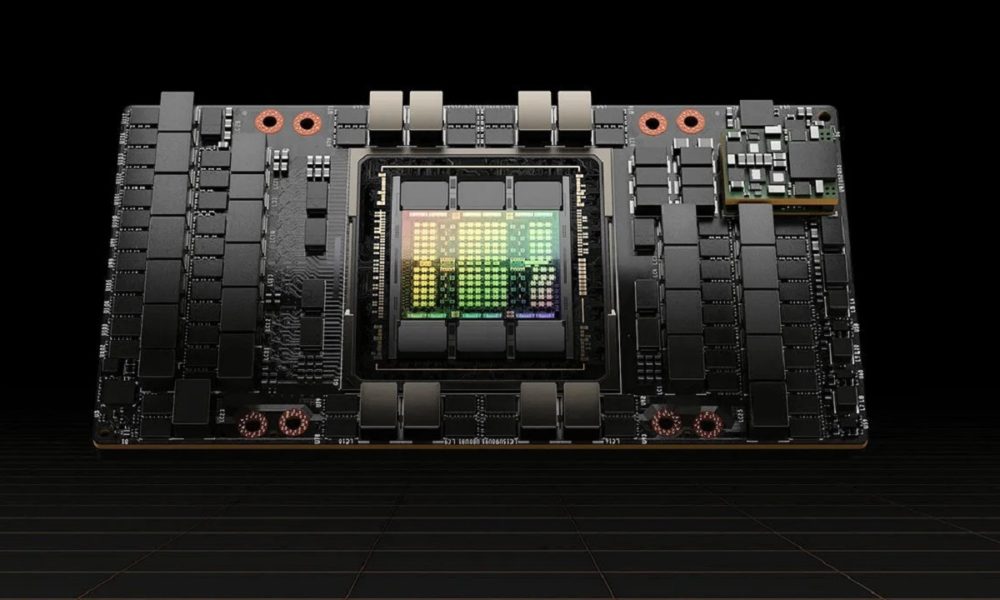
At that time we could not answer that question, but thanks to a new article that NVIDIA has shared on its official website, dedicated to developers, we have been able to see that the company is already truly harnessing the power of AI to design and develop GPUs superior to those that humans can create, and that the Hopper GPU, current flagship of those in green for the professional sector, is a clear example of this, since it has almost 13,000 instances of circuits that have been entirely designed using AI.
NVIDIA GPUs are designed mainly using what is known as EDA, that is, Electronic Design Automation for its acronym in English, but with the help of an AI that uses the PrefixRL methodology, an optimization of parallel prefix circuits using deep reinforcement learning. This allows NVIDIA to design smaller, faster, and more efficient chips that deliver higher performance.
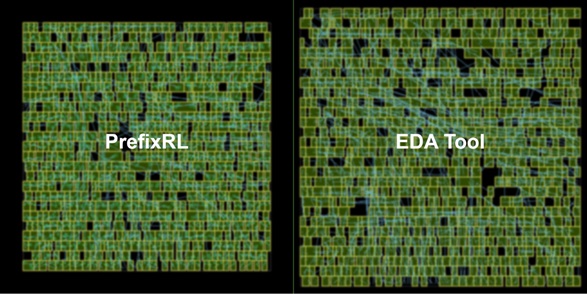
The difference at the area level is remarkable.
Compared to the standard EDA methodology the differences are substantial. According to NVIDIA, the use of PrefixRL allowed him to achieve an arithmetic circuit design that fit neatly into the “desirable” level, that is, they had a small area, high performance and low consumption, and best of all, the AI was able to reduce the total area by 25% of those almost 13,000 circuits in comparison with the design obtained through EDA.
Very interesting, but this technology is also very demanding. According to NVIDIA, for it to work optimally, it is necessary to have, for each GPU to be designed, a computing system that has 256 CPUs and 32,000 hours of work at the GPU level. To solve the problem that this high demand represents at the hardware level, NVIDIA has created Raptor, an internal platform specialized in distributed reinforcement deep learning that offers the necessary performance, and that also has high scalability. We can find more information on the NVIDIA website.



