Bad news for users of AMD processors with Zen 2 and Zen 3 architecturessince the finding of FaulTPM points out a vulnerability that, yes, it is not exploitable remotelyand that requires no less than half an hour of complete access to the system that is being attacked, which reduces its overall level of danger, although it does pose a problem in all those computers that are physically accessible by a potential attacker with the level of knowledge required to exploit this security flaw.
FaulTPM has been discovered and spread by a group of researchers from the Technical University of Berlin, who have published an article called “faulTPM: Exposing the Deepest Secrets of AMD fTPMs”. In it, which is quite complete, the nature of the bug is fully exposed and what steps an attacker must take to exploit it. Thus, with this information made public, all the necessary circumstances exist for it to be exploited for malicious purposes, which is a wake-up call for both users and administrators of computers based on Zen 2 and Zen 3 (the report does not make any reference to Zen 4so we can understand that the most current AMD architecture is not exposed to FaulTPM).
As we can quickly deduce from his name, FaultTPM affects the TPM (Trusted Platform Module) of the system, an element that became very important after Microsoft proposed it as an essential technical requirement in all those systems that wanted to upgrade to Windows 11. This is not the first time that we have encountered a security issue related to this module. About two years ago, we told you that a bad implementation of the chip could compromise its content, and much more recently, a couple of months ago, we learned of two vulnerabilities that, once again, compromised its security.
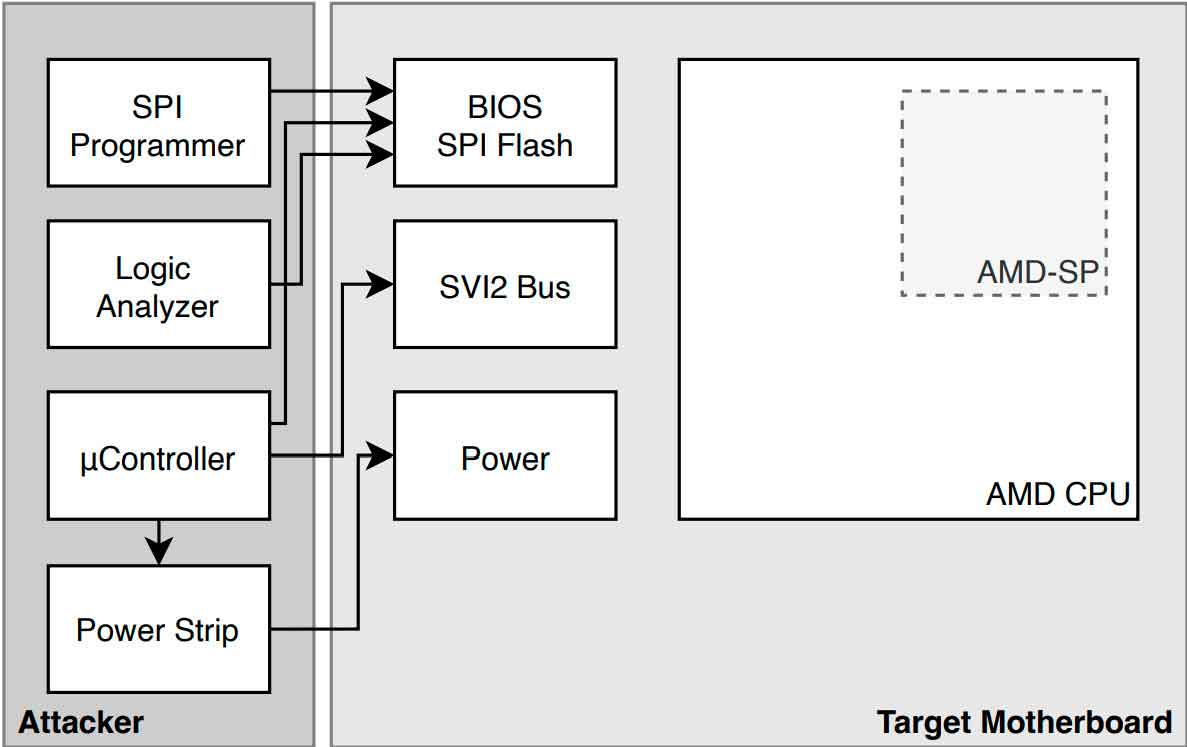
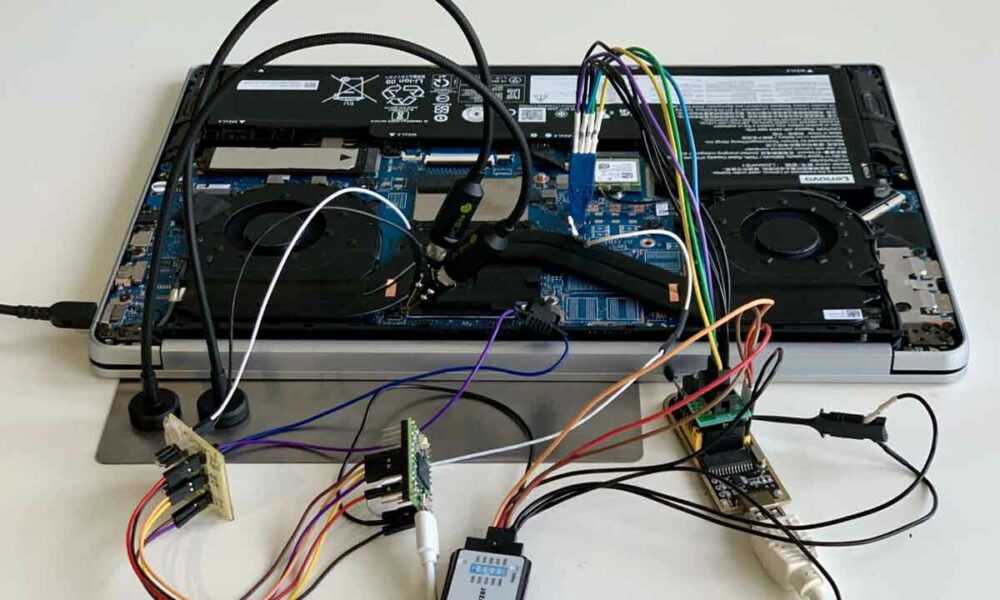
In this case, the vulnerability is exploited by voltage fault injectionwhich causes the disclosure of a unique key of the CPU of the system that is being attacked, a key with which the attacker can later access all the keys stored in the security chip, thus compromising from access to the system up to any application and service used in it (such as corporate tools, for example), which base their security on this module.
As the report reveals, the first phase of the attack requires about 30 minutes, and this operation can be carried out manually, but it can also be automated. In the second phase, the attacker will carry out multiple attack attempts in order to determine the last parameter that he needs to obtain full access and, in this way, be able to bring the payload with which he will exploit the vulnerability to the compromised system. From this point on, all content stored and/or encrypted by the fTPM will be fully accessible to the attacker.
AMD has responded to Tom’s Hardware regarding FaulTPM, stating the following:
«AMD is aware of the research report on the attack on our firmware Trusted Platform Module that appears to exploit related vulnerabilities previously addressed in ACM CCS 2021. This includes attacks carried out through physical means, typically outside the scope of mitigations security of the processor architecture. We are continually innovating new hardware-based protections in future products to limit the effectiveness of these techniques. With regard specifically to this document, we are working to understand potential new threats and will inform our customers and end users when necessary.«