Apple products have a multitude of built-in sensors, and some of them also incorporate the LiDAR sensor, that unknown. Let’s see which models have it, what is it for and what can it be used for.
Any Apple product is a work of engineering art.. They have a multitude of built-in sensors that provide the phone with a quantity of data and parameters that influence its proper functioning in any situation.
Sensors on the iPhone
simple
Firstly, we have the accelerometerwhich is capable of detecting changes in the device’s movement and orientation, allowing the device to change the screen orientation or assisting in the control of motion-based applications and games.
Another fundamental sensor is the Gyroscopewhich is the one that complements the Accelerometer on the precise orientation of the device in three-dimensional space, key for navigation apps, such as M
apas, Google Maps, etc, or augmented and virtual reality apps.
He also wears a Barometer, capable of measuring changes in atmospheric pressure, which yields data on the altitude at which the device is located. Useful data for apps that use altitude as a reference parameter and essential, for example, for the Health app, allowing us to count the floors we go up or down daily.
He Magnetometer allows you to detect the direction and orientation to which the device is heading, allowing navigation apps to know in which direction it is going, as well as allowing you to know where you are moving the device, also widely used by augmented reality apps and virtual.
It also has a Ambient Light Sensor which is in charge of measuring the ambient light and thus adjusting the brightness of the screen automatically, optimizing its display in any light situation and, incidentally, saving battery life.
And we finished with Proximity sensorwhich is used when we bring our ear and face closer to the iPhone during a call, deactivating the touch screen so that we do not accidentally press any of the buttons on the screen.
complexes
Complex sensors are understood when They are a system of sensors and not just onethose that collect and process specific information to be used later by the mobile device.
In this sense, we have the set of Facial Recognition sensors, the FaceID that we all know, that enables the identification and unlocking of our device and the authentication in the apps that use it as an additional protection measure.
Also the set of sensors for Fingerprint Recognition (Touch ID), which is still valid on some Apple devices and keyboards, which works in the same way as Face ID but with our fingerprints.
He GPS is another well-known set of sensors that enables the geolocation of the mobile, either by antennas or through the satellite network at a specific point on the globe. Loved and hated in equal parts.
Dear for helping us navigate anywhere, from one point to another, thanks to navigation apps and allowing us to know where our device is in case of loss. And hated for exactly the same reason, for reporting our position to all those apps that track us to find out what we visit and how often (although it can be disabled).
Finally, capacitive sensorswhich are that set of sensors attached to the glass of the touch screen and that detect the electrical distortion that occurs when you bring your fingers closer to the screenwhich are also electrical conductors.
That way the iPhone knows where you are pressing on the screen and that is why touch navigation on it works as smooth as if it were “magic”, as Steve Jobs would say.
The LiDAR Sensor: that unknown
What is it for?
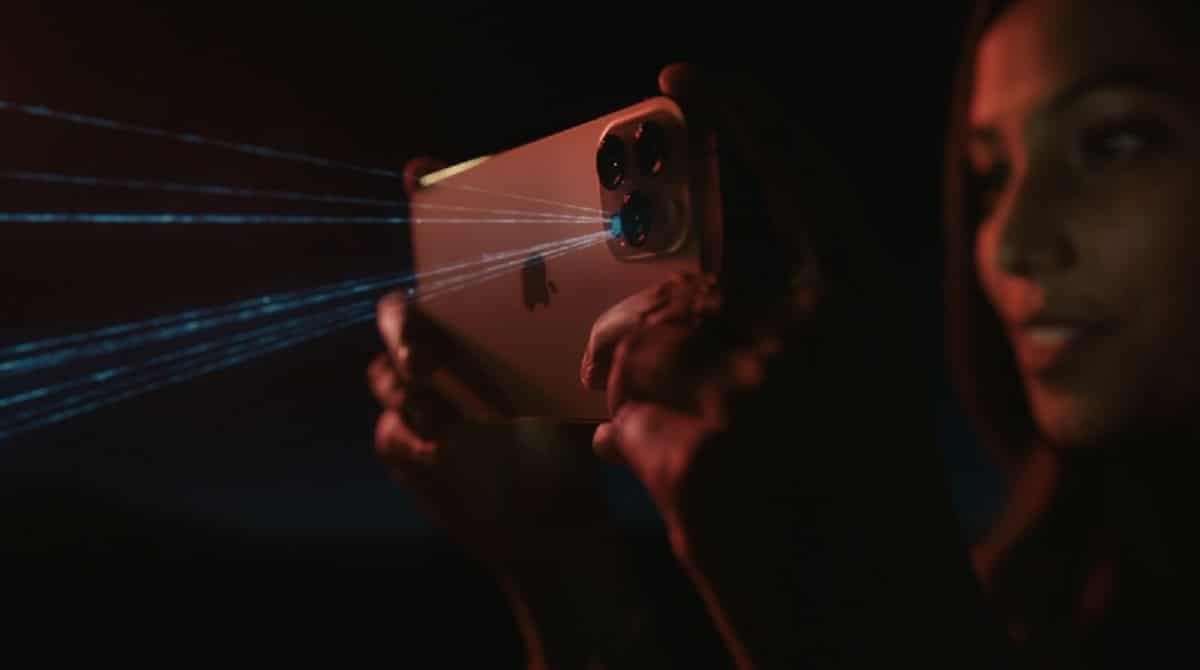
The LiDAR sensor, that unknown, made its first appearance on the iPad Pro in 2020, and the following year it jumped to the Pro and Pro Max range of iPhones. That is, from the iPhone 12 Pro and Pro Max, the LiDAR sensor is already incorporated into the Pro range.
LiDARan acronym for “Laser Imaging Detection And Ranging«, is a sensor that emits pulses of laser light and measures the time it takes for it to return after reflecting off an object. By knowing the speed of light, the sensor can calculate the distance between the emitter and the object with great precision.
By repeating this process thousands of times per second and in different directions, the LiDAR sensor can generate a detailed three-dimensional map of the environment. Its applications are very extensive. It can be used in various fields such as cartography, topography, autonomous driving or augmented reality.
We have recently seen the LiDAR sensor make an appearance again with the presentation of the Vision Pro, Apple’s mixed reality glasses. It has no less than 5 LiDAR sensors inside that allow gesture control of them and help 3D video recording with the glasses themselves. Without a doubt, those LiDAR sensors make the use of the Vision Pro a much more immersive experience.

What can it be used for?
The fact that the LiDAR Sensor is only in the Pro range devices has a fundamental reason and that is that its applications are aimed at a specific group of professionals who are the ones who can get the most out of it.
Its incorporation in the iPhone has expanded the possibilities in photography, augmented reality and camera focusso it enhances Portrait mode photography, enhances low-light photos and enables recording with the incredible Cinema effect.
But apart from that, there are already many apps that use the LiDAR sensor to map objects or to perform point cloud scans, resulting in 3D maps from which to extract a lot of information, apart from being fully exportable.
The results are amazing. A Technical Architect tells you that he is already drawing plans with point scanning through the LiDAR sensor and taking the mapping results to drawing applications where we can extract 2D and 3D plans.
And it is that this technology coupled to a mobile device such as an iPhone, Avoid carrying larger devices and allow professional results to be obtained quickly and effectively.
And that added to the processing capacity of the A14, A15 or A16 Bionic Chip that mounts the iPhone 12, 13 and 14 Pro or Pro Max, respectively, make it the undisputed leader compared to other specific devices.
Where is it located?
is maybe one of the easiest to identify when we have the iPhone in hand, since is located in the backnext to the cameras of our iPhone, and sometimes it is confused with the light of the flash, but the LiDAR sensor, as you can see in the image that illustrates this post, is in the lower part of the set of cameras.
I hope that this tour of the sensors that our iPhone incorporates, and especially of the extraordinary and yet to be exploited capabilities of the LiDAR sensor, have helped you get to know that unknown sensor that the Pro and Pro Max models have.