The first thing we are going to do is find out what the use of this program can bring us. Then we will see how to get it up and running and what are its minimum requirements for it to work. We will finish by seeing how Network Meter works to monitor our local network with examples, using one and several network interfaces.
What Network Meter offers to monitor our LAN
Network Meter we could define it as a free program Searching for network interfaces and adapters in the system for LAN monitoring. Thus, it is able to provide detailed information on each interface. Its way of operating is simple, each interface monitor has a view with simple statistics and a graphic screen that shows the time history. This would be an example of the main screen of the program to give you a better idea:
It is a tool to measure network traffic. Thus, we can use Network Meter to monitor our local area network in real time by selecting one or more network interfaces. It is an easy-to-use software in which simply to start working we will select one of the available Ethernet or Wi-Fi adapters, being able to work even with virtual ones.
In summary, we can say that it is not a complex application, and that it has been developed as an easy-to-use tool. It also offers us the inbound and outbound traffic, and also shows us the results in a graph. As for the license, it should be noted that it is free to use for both private and commercial users, so we could all use it.
Minimum requirements and use of the program
Regarding the minimum requirements, we need a computer with Windows 2000, XP, 2003, Vista, 7, Server 2008, 8, 8.1 or 10. Regarding the hard disk space, the version that we have used is 2.3.0, with 20 MB you will have enough. Therefore, on practically any computer from the last 20 years you could run this software without problems. The first thing we should do is download it for free from its website. Then you will see a screen like this:
In this case, what you have to do is click on the button Download, marked with a box and a red arrow to save it on your hard drive.
It should also be noted that, in addition to being free, it is portable. This means that once downloaded, we just have to unzip it and run it to start using it. If you do not have a file decompressor installed, Windows Explorer has one and files with a .zip extension, as is the case, can be decompressed without problems.
Get started with Network Meter
To start using this tool we must double click on the file NetMet which will be the only one we have after unzipping the file we downloaded.
The Network Meter tool to monitor our local network the first time we run it will look like this:
Do not worry if at first you see it very simple and you do not see any data on the screen. That is because we have not selected the proper options. The first thing we are going to see is the main menu with its main options, which you have marked in a red box. Here we have these sections:
- File: we have the option to refresh the results, we can also do it directly using the F5 key.
- Display: to select the network adapter that we want to monitor. You can select one or more.
- View: here we will choose the display options and the graphics update period.
- Help: used to check the version of the program and go to the developer’s website.
From the main menu we are going to see two in depth and in more detail, they are «Monitor» and «View». Next, if we click on Display We will see a screen similar to this:
Its operation is very simple, if we select an adapter that is working, we will immediately see a summary of its network traffic and current evolution. The first time you use it, we recommend simply selecting your Ethernet or Wi-Fi card. In our case it is a Gigabit Ethernet network card that I will press later. It also supports working with a virtual interface.
The next section of the main menu is View which offers us these options:
One is Update Period in which we can choose the update period in which the data is refreshed. The best thing is to leave it in normal so that it updates every second, and in fast every 0.5 seconds if we need more precise information. On the other hand, a section that I recommend activating is Interface View, then we would see the available interfaces.
Here we could do the same as in «Display«, That is, select our network interface. The only thing to keep in mind is that it will leave less space available to view the rest. Also, in that window you will be able to see the traffic that this adapter has generated in the categories of Download (download) and of Upload (rise). In addition, on the right side you have a scroll bar to see the rest of the adapters when you have more than five.
On the other hand, in the Windows task bar, for greater convenience you can find a Network Meter icon to monitor your network traffic and that gives access to the program, in case you want to leave it in the background.
Practical examples of using Network Meter
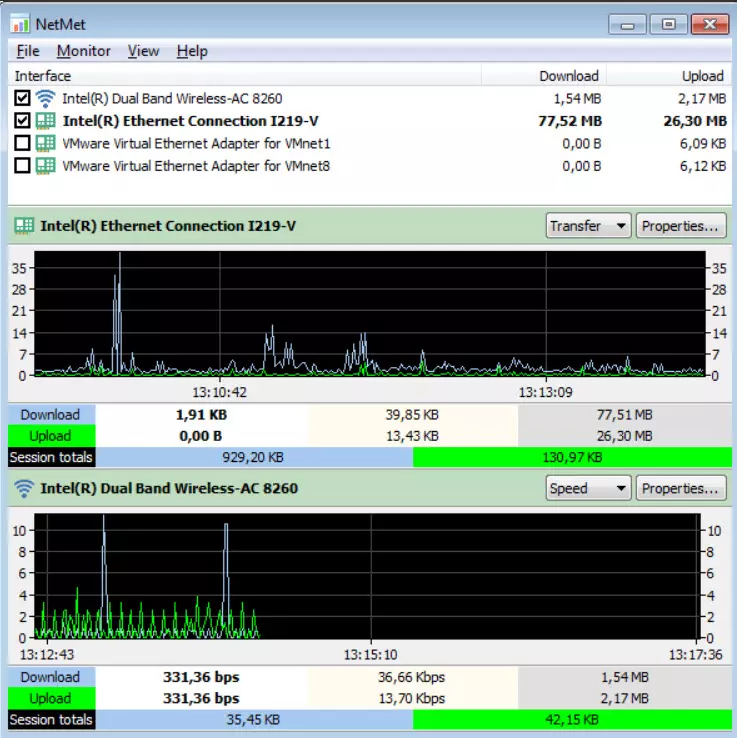
Now we are going to select our Ethernet network card, then Network Meter will show us a graph, along with a summary of my network traffic statistics.
In the place where the name of the network card appears, we can see two elements to take into account. First “Transfer»Allows us to change to see the amount of MB sent and received through the network. The second “Speed»Refers to the transfer speed measured in Mbps. Also, by clicking on the button Properties A window will open that will offer us information about the network card and its configuration.
It can also provide information from multiple network interfaces at the same time. This is ideal, for example, if you are working with a virtual interface:
When there is no more space for the rest of the network adapters to view it, you will have to see them by moving the bar that you have located on the right.
As you have seen, Network Meter allows us to monitor our local network quickly and easily, in addition, it does so in a very complete way so that we can see in detail the download and upload traffic of the different network interfaces, ideal to know what is happening. We can also see the amount of traffic exchanged on the local network and the Internet, all in a very intuitive way.