If you are looking for a list with the terminal commands for mac, you have come to the right article. In this article we show you the most useful terminal commands for Mac on a day-to-day basis to carry out actions manually without relying on the macOS graphical interface.
How to open Terminal on Mac
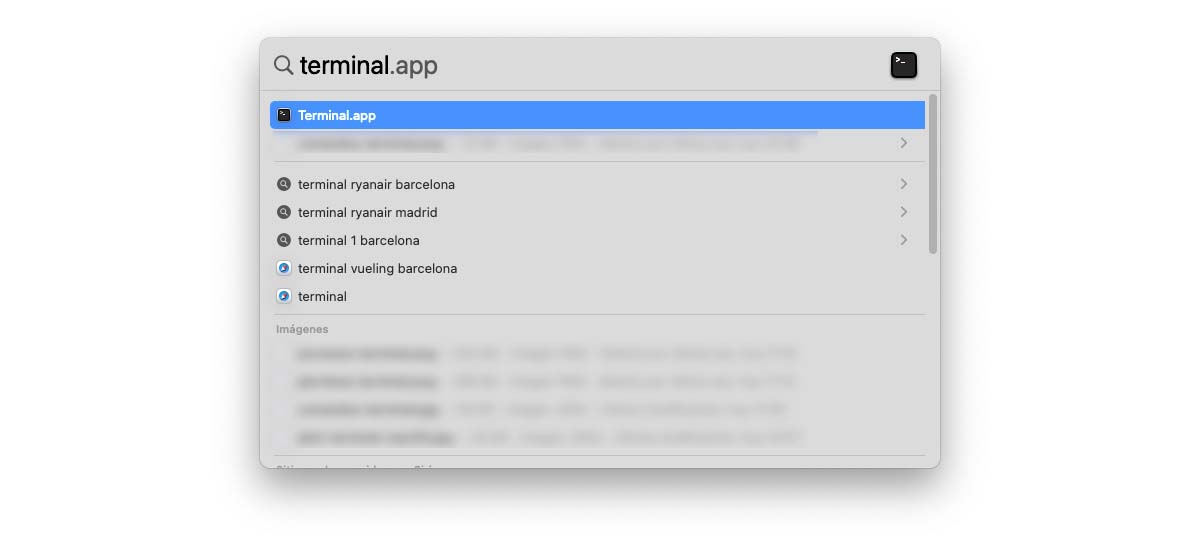
The fastest method to access Terminal on Mac is to use the keyboard shortcut Command + Spacebar, type Terminal and click on the first result.
Terminal Processes
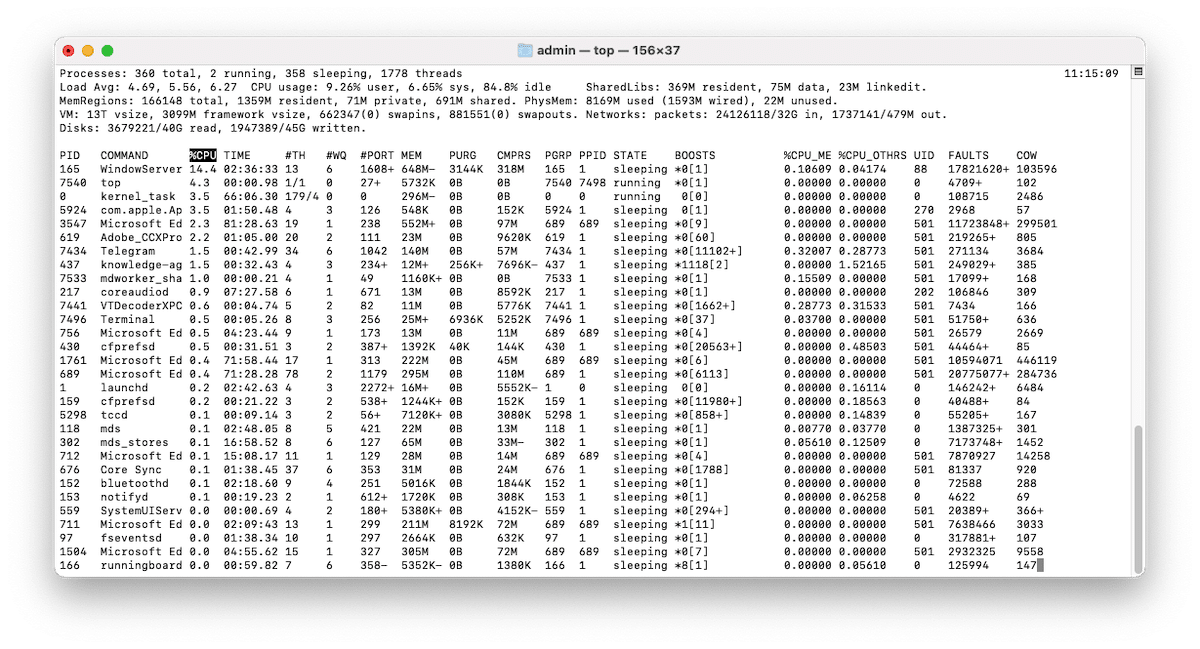
| ps-ax | Shows the processes that are currently running. The command “a” shows the processes of all users and the command “x” shows the processes that are not connected with the Terminal | |
| ps -aux | Show all processes with %cpu; %mem; page in and PID | |
| top | Shows real-time information about the processes that are running | |
| top -ocpu -s 5 | Shows processes sorted by CPU usage and updating every 5 seconds | |
| top -o rsize | Sort processes by memory usage | |
| kill PID | Exit the process with ID |
|
| ps -ax | grep |
Find a process by name or PID | |
Terminal Search
| “find |
Find all files named |
|
| to search for parts of filenames | “grep “” |
|
| Find all matches of |
“grep -rl “” |
|
Find all files containing inside
| Basic Terminal Commands | / (Forward Slash) | |
| Top level directory | . | |
| Access current directory | .. | |
| top directory | ~ | |
| main directory [command] | sudo | |
| Run command with superuser security privileges [file] | elder brother | |
| Open the Terminal editor [file] | open | |
| [command] open a file | -h | |
| Get help on a command [command] | man | |
Shows the help manual of the command
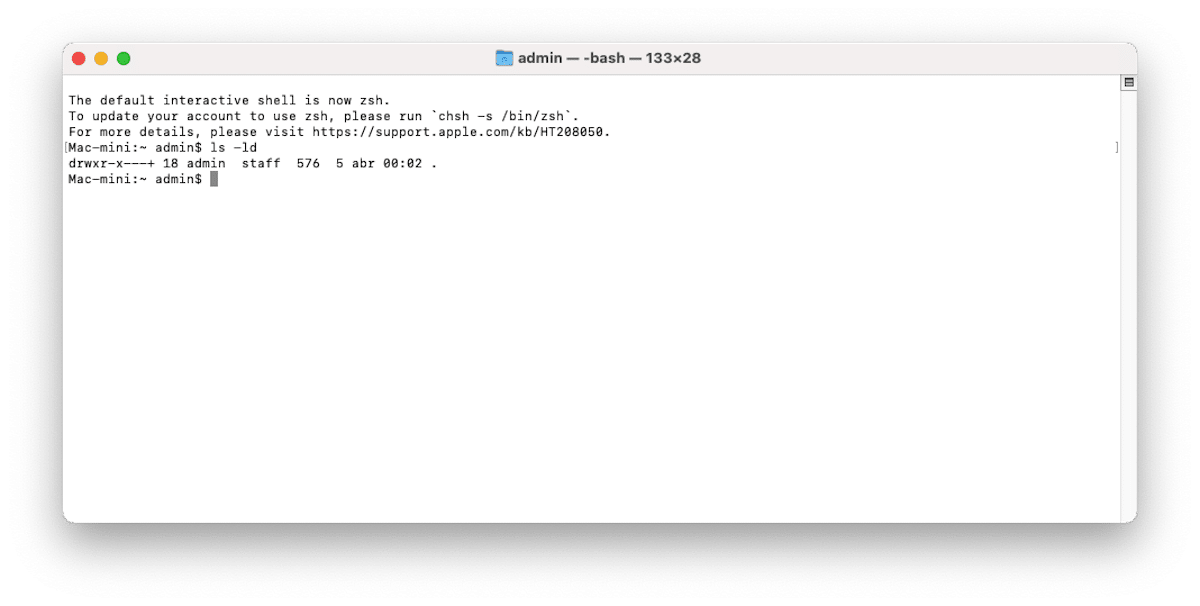
| Permissions in Terminal | ls -ld | |
| Show the default permission of a source directory | ls -ld/ |
|
| Show read permissions; write and access of a given folder | chmod 755 |
|
| Change the permission of a file to 755 | chmod -R 600 |
|
| Change the permission of a folder and all its contents to 600 | chown |
|
Change the ownership of a file to user and group If we add the command “-R” the contents of the folder will be included
| macOS Terminal Files | du | |
| Using the list for each subdirectory and its contents [folder] | du-sh | |
| Readable output of all files in a directory | du -s | |
| Show one entry for each specified file | du -sk* | sort -nr | |
| List files and folders (summarizing size including subfolders). We can substitute sk* for sm* to list the directories in MB | df -h | |
| Shows the free disk space of your system | df -H | |
| Calculate free disk space in powers of 1,000 (instead of 1,024) | mkdir |
|
| Create a new folder called |
mkdir -p |
|
| Create nested folders | mkdir |
|
| Create multiple folders at once | “mkdir “” |
|
| Create a folder with a space in the file name | rmdir |
|
| Delete a folder (only works with empty folders) | rm -R |
|
| Delete a folder and its contents | touch |
|
| Create a new file without any extension | cp |
|
| Copy a file to the folder | cp |
|
| Copy a file to the current folder | cp |
|
| Copy a file to the folder and rename the copied file | “cp -R |
|
| Copy a folder to a new folder with spaces in the file name | cp -i |
|
| Warns you before copying a file with an overwrite warning message | cp |
|
| Copy multiple files to a folder [folder path][new folder] | ditto -V |
Copy the contents of a folder to a new folder. The “-V” command displays a status line for each copied file.
| Access and delete files and folders with Terminal | rm |
|
|---|---|---|
| Delete a file permanently | rm -i |
|
| Delete a file requesting confirmation | rm -f |
|
| Force unconfirmed deletion of a file | rm |
|
| Delete multiple files without confirmation | mv |
|
| move/rename | mv |
|
| Move a file to the folder (overwriting the existing file with the same name if it exists) | mv -i |
|
| The “-i” command displays a warning that it will overwrite the destination file. | mv *.png ~/ |
|
| Move all PNG files in the current folder to a different folder | CD | |
| home directory [folder] | CD | |
| change directory | cd ~ | |
| main directory | CD/ | |
| root of unity | cd- | |
| Previous directory or folder you last navigated to | pwd | |
| show working directory | CD.. | |
| Upload to parent directory | CD../.. | |
| go up two levels | ls | |
| Show the name of the files and subdirectories of the directory | ls -C | |
| Show the name of the files and subdirectories of the directory in columns | ls -a | |
| List all entries (including those with .(dot) and ..(double dot)) | ls-1 | |
| Show the list of files in the format of one entry per line | ls -F | |
| Show a / (slash) immediately after each path that is a directory | ls -S | |
| Sort files or entries by size | ls -l | |
| List in long format. Includes file mode; the name of the owner and the group; the date and time the file was modified; the path name; etc. | ls -l / | |
| File system list from root with symlinks | ls -lt | |
| List of files sorted by modification time (newest first) | ls -lh | |
| Long listing with readable file sizes in KB; MB or GB | ls-lo | |
| List of file names with size; owner and flags | ls-la | |
Detailed list of directory content (including hidden files)
| Keyboard shortcuts in Terminal | Tab | |
| Autocomplete file and folder names | Ctrl + A | |
| Go to the beginning of the line you are typing on | Ctrl + E | |
| Go to the end of the line you are typing on | Ctrl + U | |
| Delete the line before the cursor | Ctrl + K | |
| Delete the line after the cursor | Ctrl + W | |
| Delete the word before the cursor | Ctrl + T | |
| Swap the last two characters before the cursor | Esc + T | |
| Swap the last two words before the cursor | Ctrl + L | |
| clear the screen | Ctrl + C | |
| Stop whatever is running | Ctrl + D | |
| Exit the current shell | Option + → | |
| Move the cursor one word forward | Option + ← | |
| Move cursor one word back | Ctrl + F | |
| Move the cursor one character forward | Ctrl + B | |
| Move the cursor back one character | Ctrl + Z | |
| Put what is running in a suspended background process | Ctrl + _ | |
| Undo last command | Option + Shift + Cmd + C | |
| copy plain text | Shift + Cmd + V | |
| paste the selection | exit | |
End a shell session
| terminal ping | ping |
|
| Ping the host and display its status | whois |
|
| Obtain whois information of a domain | curl -O |
|
| Download a file over HTTP; HTTPS or FTP | ssh |
|
| Establish an SSH connection to |
scp |
|
| Copy |
harp | |
| Shows a list of all devices on your local network including the IP and MAC address of all devices | ifconfig en0 | |
Shows the IP and MAC address of your device
| command history | Ctrl + R | |
| Search for previously used commands | history | |
| Shows the commands that we have previously written[value] | ! | |
| Execute the last used command that starts with a value | !! | |
Run the last command used
It may interest you