- The P-Cores are large cores that offer great performance, but in exchange for being less energy efficient.
- E-Cores are smaller cores, allowing Intel to fit more in the same space and have lower power consumption.
Depending on the Intel Core 12 model, the number of P-Cores and E-Cores varies, but we must clarify that both work in unison and in a coordinated manner. For the latter, they make use of a third-level 30 MB last-level cache, which not only gives access to the same memory space to both types of cores, but also allows them to work together in the execution of the processes to be executed. .
Intel Core 12 and Amdahl’s Law
To understand what is intended to be achieved with the design of the Intel Core 12 we must bear in mind that every program is divided into two parts:
- A part that runs in series, on a single processor and therefore it will need to be as fast as possible to accelerate its execution, so this part of the programs in the Intel Core 12 is handled by the P-Cores.
- The other part that can be run in parallel, so adding more processors will speed up the resolution of the same more than not having a CPU. The E-Cores are in charge of this type of task.
Nor can we forget that on a PC there are more tasks than we see and the correct assignment of them is important, it may be that while you are playing a game the mail application is updating the inbox. Gaming is a foreground process and email management is a background process, so it’s best to assign those secondary tasks to a less powerful processor.
P-Cores vs. E-Cores in single wire
Starting with the P-Cores, which are the high-performance cores, we find that their L2 cache is local to each processor, while the E-Cores have this level shared between several cores. Keep in mind that the first two cache levels are not shared between both types of cores.
But what interests us is the performance, and equal to clock speed we find that the P-Cores obtain 28% additional performance compared to the tenth generation of Intel Core processors, while the E-Cores are 1% per above with respect to the same generation. So the E-Cores are not cores with a power worthy of a netbook or any very low consumption system, but their single-thread performance is at the level of the Comet Lake.
Although because the E-Cores in Intel Core 12 are designed with a view to energy efficiency, they not only work at a lower clock speed, but also do not have support for HyperThreading.
Performance per Watt, PL1 and PL2
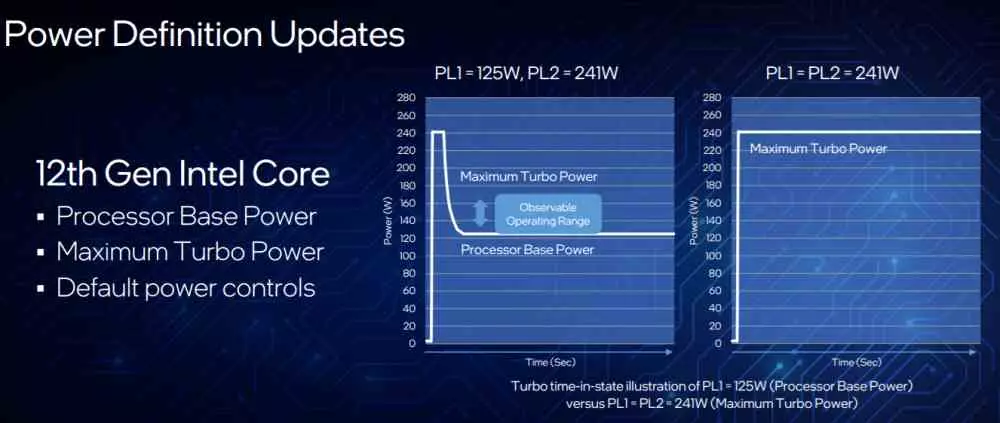
One way to measure the performance of one processor compared to another is to see how many watts or watts they consume to perform the same task. In the case of the Intel Core 12 we have two consumption profiles, in the so-called PL1 the processor consumption is set at 125 W, while in PL2 it is at 241 W.
Now, both power states combine to result in overall power consumption of up to 241 watts for higher-end CPUs, a lower figure than its counterpart and predecessor.
According to Intel, if the Intel Core i9-12900K is compared with the i9-11900K, the former obtains with only 65 W the same performance as the latter with a consumption four times higher. This is a leap in efficiency that we did not see since the leap from Pentium IV to Core 2. Already in PL1 mode, the new Intel processor achieves 30% more performance than the previous generation with twice the consumption already almost equal TDP an additional 50%.
The increase in efficiency comes in two ways, on the one hand by the use of a new manufacturing node that always gives advantages in consumption and clock speed, the second is by the use of a hybrid or heterogeneous architecture.
Performance in applications
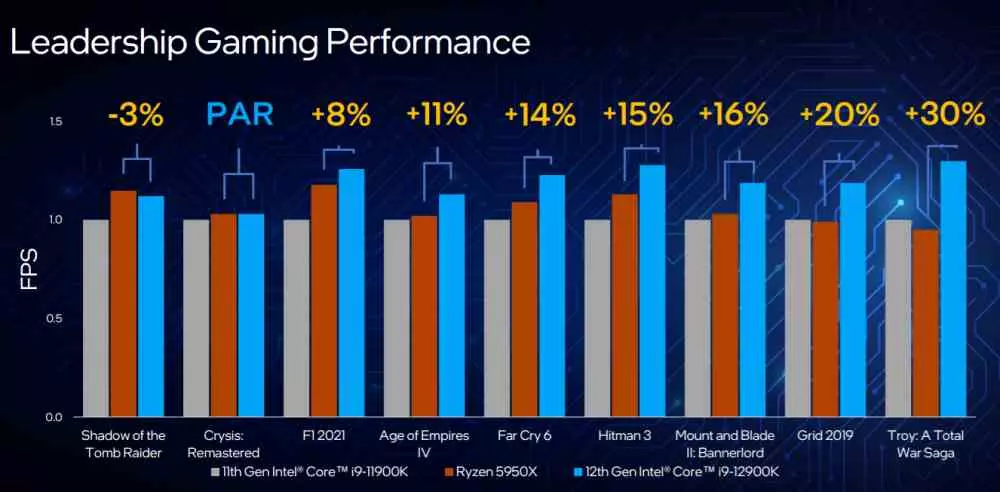
Intel has also given the performance of the Intel Core i9-12900K compared to its direct rival, the Ryzen 9 5950X in several different types of applications. Starting with the games, we can see an increase that goes from 3% in the case of Shadow of the Tomb Raider to 30% in Troy: Total War Saga.
If we are going to the content creation applications, the comparison that the blue brand has made has been between the i9-12900K and the i9-11900K, where you can see how in the PugetBench under Premiere Pro it reaches an additional 32%, but it is that in After Effects it manages to double performance.
Intel Thread Director
The control unit is the most important part of a CPU, after all, it is in charge of two of the stages of the instruction cycle: the data capture and the decoding of the instructions, the latter includes the appropriate assignment to the units. of execution.
But in a hybrid or heterogeneous system it is also important where we assign each process to run as efficiently as possible. That is why Intel has added a new function to the control unit of the Intel Core 12, which measures the execution time of each process to execute and recommends to the operating system, Windows 11, where it is better to execute each process , if in the P-Cores or the E-Cores.
In addition, it not only has the time cost of each instruction, but also the energy cost, since not all instructions consume the same amount. The objective is that a process that requires high performance does not go to the E-Cores, which would lead to a slower execution, or that a light process does not go to the P-Cores, it would waste them.
The Intel Core 12 processor range
The initial range of the Intel Core 12 is divided into six different CPUs, three configurations with two variants, with and without an integrated GPU, although otherwise they are totally the same with respect to their pair. Another highlight is the Intel Core i5-12600K and i5-12600KF variants where the overclocking functions of the Intel Turbo Boost Max 3.0 have been disabled.
Overclocking
A very important element of a processor is the ability to vary its clock speed and since it is the first CPU under the Intel 7 node there have also been improvements at the manufacturing level that allow it to achieve high clock speeds with less with a lower consumption compared to previous generations of Intel processors, especially on the desktop where this node is used for the first time.
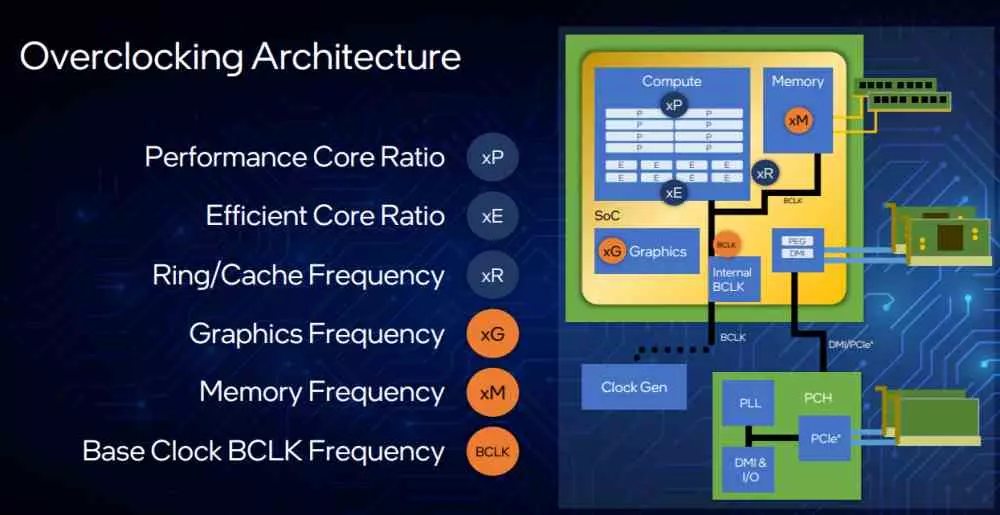
The overclocking system of the Intel Core 12 allows the following changes to be made to both the P-Cores and the E-Cores:
- Ability to enable and disable the execution of AVX instructions.
- HyperThreading can be disabled in the P-Cores if necessary in exchange for being able to gain more speed.
- You can adjust the voltage at the individual level of each of the cores, so we can lower the clock speed of some to increase that of others.
- We have advanced options for overclocking that allow us to vary values such as TjMax, PLL and BCLK.
- Ability to connect and disconnect cores individually and separately from the rest.
Support for DDR5 and XMP 3.0 memory
The Intel Core 12 are the first processors for PCs on the market that support DDR5 memory, specifically they support DDR5-4800 modules, although they are compatible with faster memories, for this the processor memory controller is set to half speed to match the times of the signal, so with the type of DDR5 RAM that these processors will work best is with the DDR5-4800 in terms of latency time of the instructions.
The Alder Lake-S architecture inherits all the capabilities of its predecessors with respect to DDR4 memory, with which it is also compatible, and moves it to the new standard by creating version 3.0 of its standard for memory overclocking. And is that one of the novelties of DDR5 memory is the fact of having the voltage control in each memory module, which has forced Intel to develop XMP 3.0. With this, the number of profiles available for Intel Core 12 has gone from 2 to 5.
I / O on Intel Core 12 and the Z690 chipset
Nowadays, all CPUs have a series of I / O interfaces integrated inside them and this is where the Intel Core 12 are once again the first to adopt a technology, in this case PCI Express 5.0 that doubles in bandwidth. to version 4.0. The new processor integrates 16 lines, so it is ready for the new generation of graphics cards for gaming that will be released in 2022 and will make use of this standard.
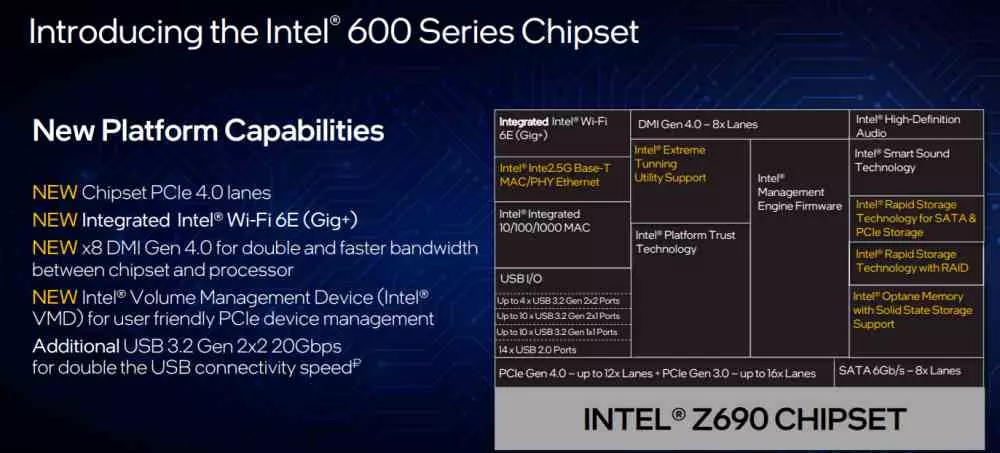
Although we cannot forget that every processor goes a socket, in this case the LGA1700 and every socket goes to a motherboard with a specific chipset and Intel has opted for the 600 series chipsets being the most complete of all the Z690. The communication with which is done with the DMI 4.0 interface, which means doubling the bandwidth between the CPU and its Southbridge.
The I / O interfaces provided by the Z690 chipset to the Intel Core 12 are the following:
- Integrated WiFi 6E (Gig +) radio.
- Add 12 PCI Express 4.0 lanes to which 16 must be added for 3.0 speed.
- Regarding USB connectivity, it has support for version 3.2 of the standard with the following configurations: 4 2 x 2 ports, 10 2 × 1 ports and 10 1 × 1 ports. It also has support for up to 14 USB 2.0 ports.
- 8 SATA-III lines.
The chipset also incorporates other Intel technologies such as Platform Trust Technology, essential for running Windows 11, but also support for Rapid Storage and Optane technologies.