We are sure that, on some occasion, you will have to manually configure the mobile network options to adjust certain settings that we can make, such as forcing the use of only 4G networks instead of leaving it automatic, which includes 5G networks but They make the battery last significantly less.
Mobile networks and their different generations
Currently the most modern networks are 5G, which refers to fifth generation mobile networks. With each evolution, both higher upload and download rates have been achieved along with a reduction in latency. We can consider 5G as an important evolution because it is the first that, due to its low latency, will allow us to interact in a different way thanks to the IoT (Internet of Things). For this reason, we are moving from IPv4 to IPv6 because the former no longer has enough IPs available. The reason is that we increasingly need more individually connected devices in factories, in cities and even in our own homes. The evolution does not stop, work is already underway on 6G and in a few years we will have the first devices.
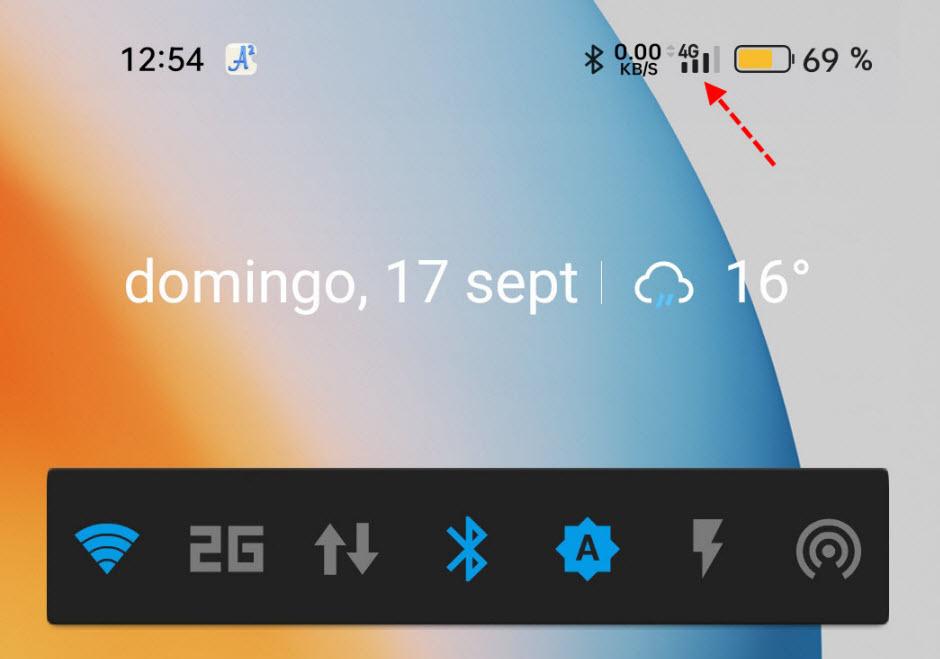
Here you have a reference of a smartphone connected to a mobile network. The lines refer to our coverage and the larger they are, the better it will be. Then on top of that we have the network generation to which we are connected and the higher it is, the more speed we can obtain assuming we have good coverage. Nowadays Android phones have this nomenclature:
- 2 G: for second generation networks.
- 3G, h and H+ They would be the third ones, they were the most common networks more than 15 years ago.
- 4G and 4G+ The fourth generation networks are widely used today, and with great coverage throughout the Spanish territory.
- 5Gthey are the latest generation, they are the fastest, but we still do not have much coverage throughout Spain.
In the example above you can see that we are connected to a 4G network and that we have good coverage. We must keep in mind that today all smartphones have a 4G connection, however, not all models have a 5G connection per What we cannot connect to these networks with all models.
First steps with a mobile network on Android
If we want to configure mobile networks in a more personalized way, we can make a series of Settings that we will discuss. We are going to do it with a smartphone whose operating system is Android 13. The next step we are going to take is to go to Settings, Mobile Network.
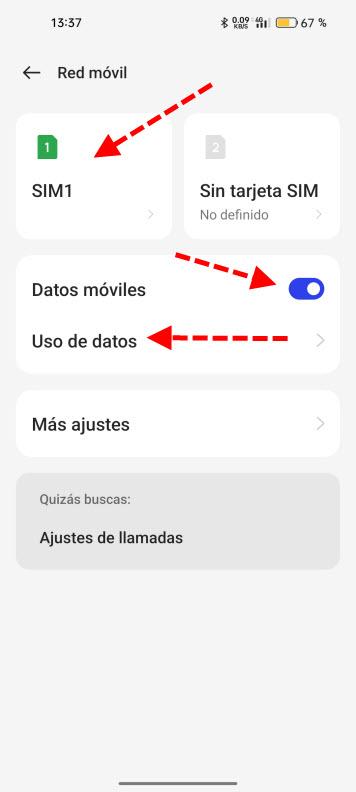
Next, a screen like this will appear with which we can start working:
Here we are going to talk about the following functions:
- SIM 1 and SIM 2: Nowadays most mobile phones are DUAL SIM. This means that we can have two phone lines on our smartphone. Each can be configured individually with its own parameters. For example, you can have two SIM cards from different providers or countries.
- Mobile data: Used to activate or deactivate this type of networks. If we are on a Wi-Fi network we do not need them to be activated. Also if we are short on battery or want to save data we can deactivate them.
- Data usage: If we want to know the mobile data consumption we have made, it is usually very similar to that of the ISP or Internet provider app.
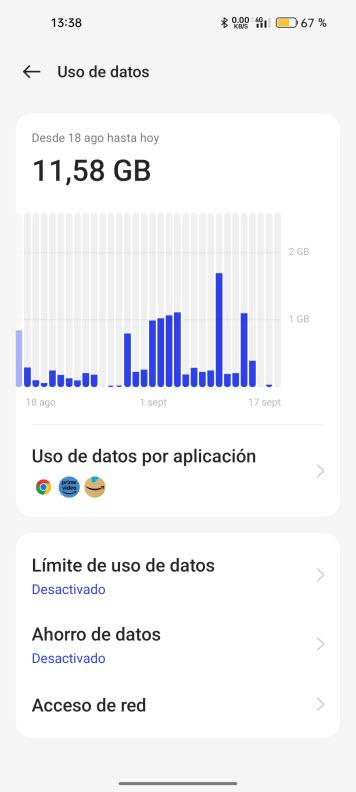
If we click on “Data usage” a screen like this will appear:
Here what we have to do is establish the billing period of our ISP. Then it offers us possibilities such as limiting data usage per day so that we do not run out of data. It also allows us to activate data saving at the cost of sacrificing that notifications arrive later and also allows us to choose which app can connect using mobile data.
SIM card settings
The moment we click on SIM 1 We can configure the parameters that affect our card.
Now we are going to talk about the following sections:
- Data roaming It is usually activated when traveling abroad. When we activate it we connect to the mobile network of another operator. Depending on the country we are in, additional charges may or may not be applied to the invoice. In the case of EU countries there are a series of agreements that allow you to make calls and use mobile data up to a certain limit at no additional cost.
- 4G calls either VOLTE that allow us to make voice calls with higher sound quality using this type of networks at no additional cost.
- Wi-Fi Calling either VoWifi If we have a Wi-Fi network with an Internet connection, even if we do not have coverage, we can continue sending and receiving phone calls. Both in this case and in the previous one, a smartphone that supports it is required in addition to the supporting ISP for your model.
- Preferred network type in which we can choose if we want to connect if there is availability to a 2G, 3G or 4G network, etc. When there is a new generation like 5G, sometimes it is advisable to limit it to 4G. The reason is that you are more likely to lose 5G and have to change mobile networks more often, which reduces battery life. This same thing has already happened with 4G networks, now with 5G, although to a lesser extent, and the same thing will surely happen when 6G comes out.
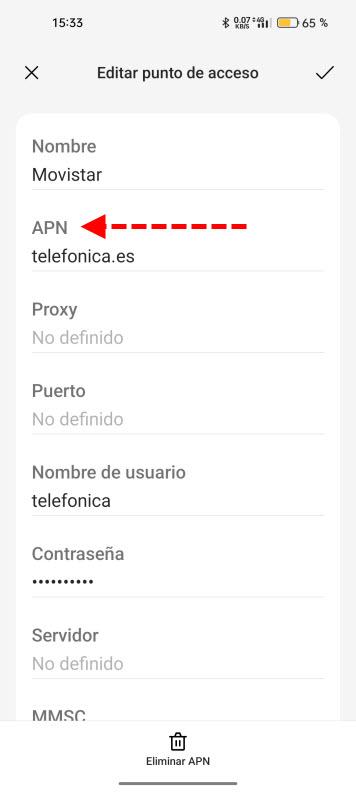
- Access point names It is the place where we can manually enter the connection data and more from our ISP.
- Operator: we can see the available networks and choose one of our ISP’s.
How to configure mobile networks
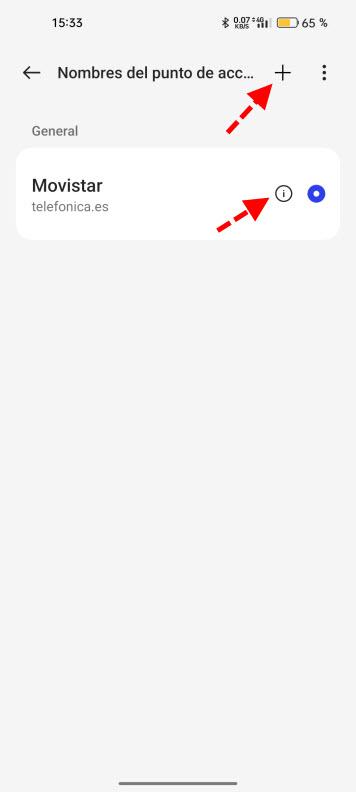
Now it is not so common to have to configure your mobile connection data, but there may be times when you need to do so. This is done through the section Access point names that we saw before. It can also be called APN or one similar to the one we mentioned before, but this will depend on the manufacturer. If we do so, a screen like this will appear:
in the symbol + It will allow us to create new access points. Thus, in the event that it did not work well, we could return to the previous one or, if there is none, create it previously. If we edit it by clicking on the ““” We can modify its parameters in case any change or we want to do tests.
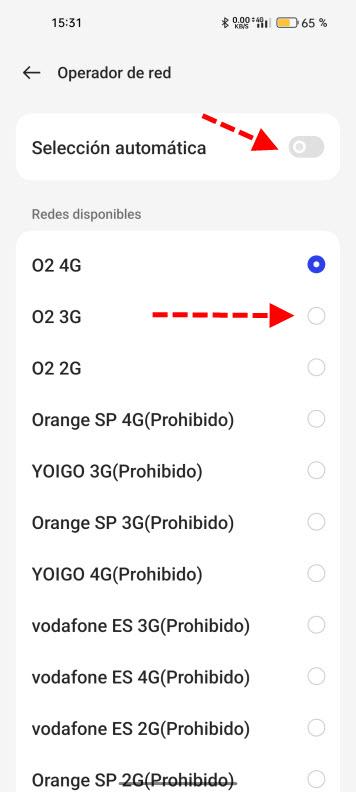
Here you have how to configure the APNs of the most common ISPs such as Movistar, O2, Vodafone, Lowi, Orange, MásMóvil, Pepephone and Simyo. It is simply to enter the data that they indicate in the corresponding sections. We also have in the section Operator a place where we can manually select the mobile network we want to connect to. The first thing we have to do is deactivate Automatic selection and after a short period of time it will show you the available networks.
Those that say prohibited will not let us connect and we should not select them just in case. This can be useful specifically in an area where we constantly lose coverage or lose stability. In the event that 4G works well at times even if the speed is reduced a little, it may be interesting to choose your provider’s 3G. Sometimes a stable 3G with many coverage gaps is better than a 4G with a coverage gap that gets stuck from time to time or loses the connection.
Finally, this is to be used as a last resort, then the ideal is to change it again Automatic selection. The reason is that later if you change location you lose 4G, 5G and the rest of the modalities, and if by chance 3G goes out you could be left without coverage.