He Task Manager Windows (the task manager) is one of the oldest and most useful applications in Microsoft systems. It is intended for medium-advanced or professional users who want thoroughly control the operation of your equipment or solve some problems that derive from its use.
Microsoft extensively renewed it in Windows 10 with the addition of some functions and greater integration with the system core and main applications, something that has been completed in Windows 11, leaving us with a really interesting tool once we know its capabilities. An ordinary user usually uses it only for its best-known function, such as end a frozen appbut its uses go much further as we are going to show you.
Access and uses of the Windows Task Manager
Accessing this tool is extremely simple and can be done in several ways, including the use of keyboard shortcuts. We review them:
- Ctrl + Alt + Delete. This is the method that almost everyone knows, but it is not the fastest because in Windows 11 it does not start directly and you will have to do an extra click to start it.
- Ctrl + Shift + Esc. More direct than the previous one, it immediately launches the task manager and also has the advantage that due to the position of the keyboard it can be executed with one hand.
- Taskbar. If you right click the mouse on the taskbar there is an option to access the manager.
- advanced user menu. Another quick access using the mouse. Right click on the start button to access the advanced menu and you will also find this Task Manager.
- Execute. If you are used to using commands, press the Win + R keyboard shortcut and type “taskmgr”.
- Search. Simply write “task” or “tasks” in the general search engine and you will see access to this tool.
As for functions, as we said, the best known is ending a frozen application. Just open the manager, right click on the application and click on “end task”.
Check why the app is frozen
What is less well known is a function called “analyze” that can help identify the problem and avoid having to kill the application by brute force, which can result in data loss. It is available in the details tab.
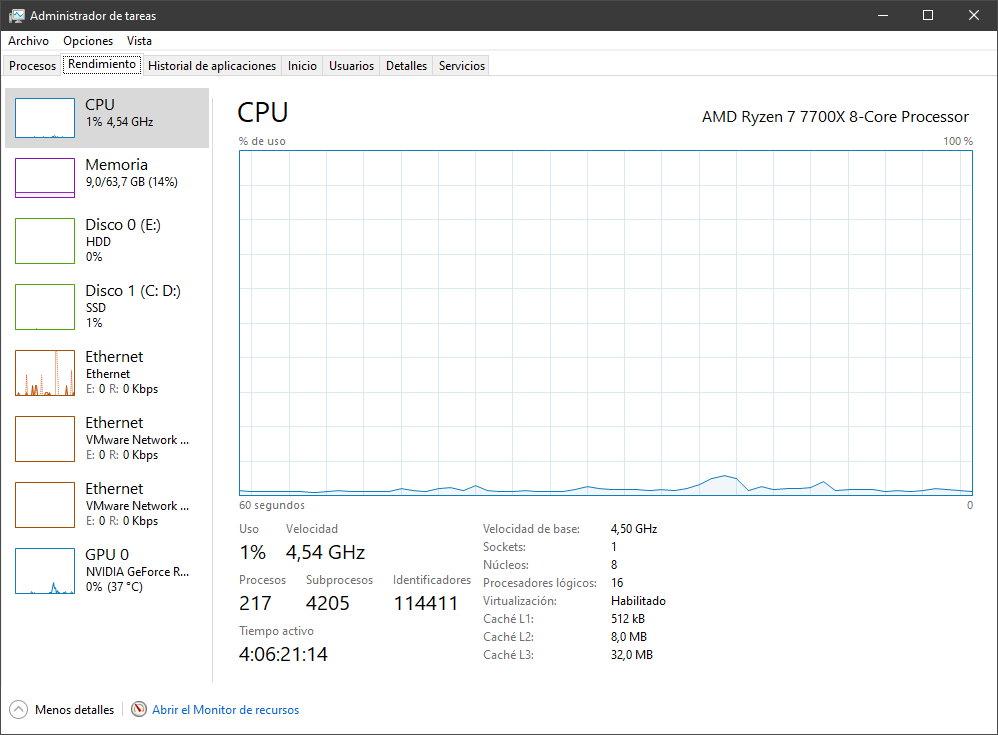
Performance and resources
This is where the Windows 11 task manager really shines. It not only provides an overview of all running processes and applications but has various tools to effectively monitor system performance and how resources are allocated. It includes a lot of information, from the resource monitor (RAM, processor, graphics cards…) that offers data visualization in real time; diagnostic information with logs that you can share for evaluations; network details and other resources of interest.
Windows explorer restart
Sometimes there are some parts of the operating system that do not respond (taskbar, file explorer, Start, etc.), while other applications continue to run correctly. Restarting the PC usually solves the problem, but restarting the browser may be enough. The task manager has a special action for it. If you use it, it will end the task and restart automatically.
Windows Application Management
The task manager is far from the best window management tool but it does have a couple of actions that can be useful. To access them, click the dropdown arrow next to the one you want to manage. The ones that work offer five actions, from bringing to front, maximizing, minimizing, or ending the task.
Online search for suspicious processes
You may sometimes see unknown processes in the task manager. Most of them will be legitimate, but if you don’t trust it, you can check it by clicking on the suspicious process and activating the online search. This will start a browser search for the application name and process name and help you determine whether or not it is safe or malicious.
Additional columns for more details
By default, the new Windows 11 Task Manager only shows five columns when listing processes: Name, CPU, Memory, Disk, and Network. While these are the most important, you can actually add up to six more columns simply by right-clicking on the header area. All of them can be useful in the right situation, particularly the process name because it makes it easy to detect suspicious applications by their process name.
Switch between values and percentages
When browsing the list of processes, the CPU column can show percentages, but in the other three default columns you can change them to absolute values, more useful in some situations. Just right click on any process, go to the resources submenu and you can switch between them.
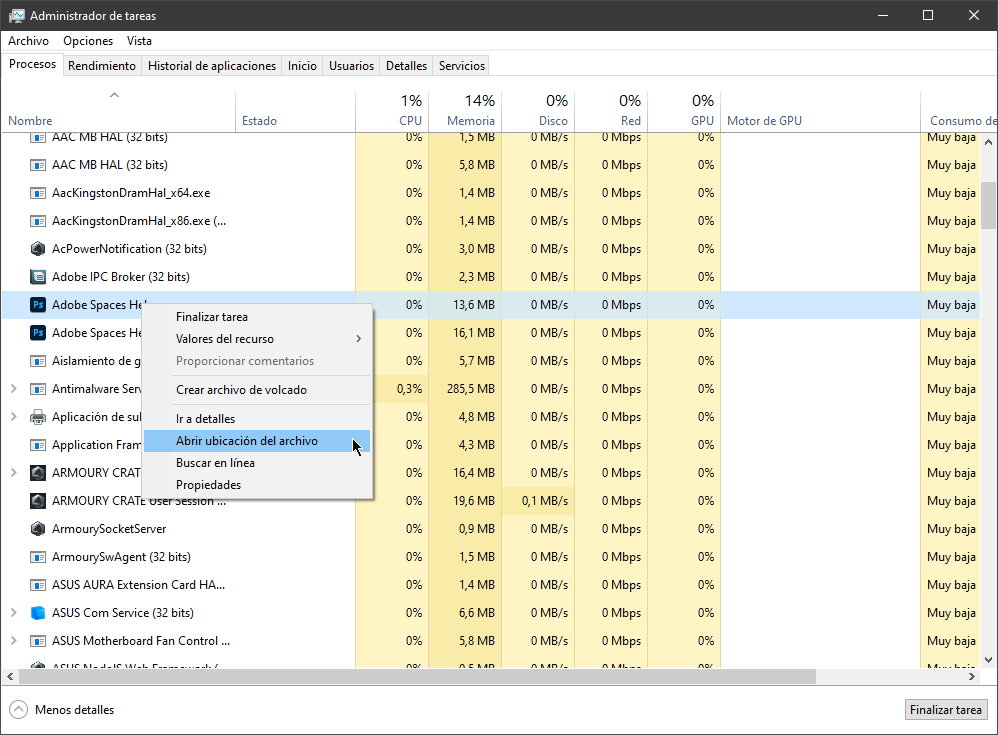
Find out the open application file
Sometimes it is difficult to know the installation location of a particular program. The file explorer is the general option, but if the application is being used, you can access it from the task manager in record time. Just click on any process and select “open file location”. This will take you directly to the folder that contains the executable file of the process. It works for apps, background processes, and Windows processes. Quick and practical.
Start the command prompt directly
In the task manager you can go to the File menu and select “run a new task” to launch the run dialog. Most people who use this tool know about it because it’s one of the ways to manually restart a frozen browser in earlier versions of Windows. What not everyone knows is that you can access the Windows console in the same way simply by holding down the Control key. Very useful.
Starting the System Configurator
In Windows 11, if you run the “msconfig” command to configure the system, you will see that the startup function has been moved to the task manager. It is the tool that allows us to configure the applications that will start at startup. The tool offers information on the impact of each application on system performance and allows you to disable them at startup. If your PC takes time to boot up or runs slower than usual, disable all non-essential applications/services from startup.
What if I use Windows 11?
Access to the task manager in Windows 11 occurs in the same way as in Windows 10. Just right-click on the start button (or on the taskbar) to access the advanced menu and there you will see a shortcut to the task manager.
Although the big changes were implemented in Windows 10, Microsoft has been improving it with the different system updates, especially in the visual section. You can find all the functions discussed above and some new ones. Equally useful on both systems, as you may have seen, it can do much more than end a frozen application that crashes the system (the best known function) and is an advanced management tool to thoroughly control the operation of a personal computer or solve some problems that derive from its use, nothing abnormal in Windows systems.