In this way, we can access both the files hosted on both machineslike resources, use the copy and paste function among other useful functions.
How to create a portable virtual machine
The first thing that we must be clear about before continuing is to know that it is a portable application. A portable application is an application that runs on a computer no need to install. In other words, we can run it on any computer without modifying the computer’s registry.
Once we are clear that it is a portable application, the time has come to talk about which application we are going to use. Of all the options available on the internet, the solution that offers us greater quality, performance and, above all, support, is found in VirtualBox.
Download VirtualBox Portable
Oracle, the company behind VirtualBox, unfortunately does not offer us a portable version of VirtualBox, so we will not be able to download this version from its official website.
However, we can make use of Portable VirtualBox, an application whose code is available on GitHub, which creates a portable version of VirtualBox to run on any computer without having to install the application. This application is only available for Windows, so we will only be able to run it in Windows environments, never in Linux or macOS.
In order for the application to create a portable version of VirtualBox, we must not have installed the application on our computer, since, otherwise, when you run it, it will automatically open the application. Once we have downloaded the application to our computer, we run it by clicking twice on the icon and select the path where we want to create the portable version of VirtualBox.
Next, we select the interface language and wait for the application to open. In the next step, select the folder where we have unzipped the Portable VirtualBox application that we are running and select what type of version of VirtualBox we want to download (32 or 64 bits).
Finally, click on Download VirtualBox installation files. Portable VirtualBox downloads the version of VirtualBox from the Oracle website, so it is not a modified version that may contain any type of malware. Once the process is finished, click OK to create the portable version of VirtualBox.
Once the process is finished, we have already created a portable version of VirtualBox. This portable version is not based on the latest available version of VirtualBox, however it allows us to run it on both 32-bit and 64-bit Windows operating systems. It should be remembered that, as of version 6.0, VirtualBox stopped offering support for 32-bit Windows computers.
Create a portable virtual machine with VirtualBox
Once we have created the portable version of VirtualBox, we must copy the directory to the external storage unit where we are going to use it and from where we are going to create a virtual machine.
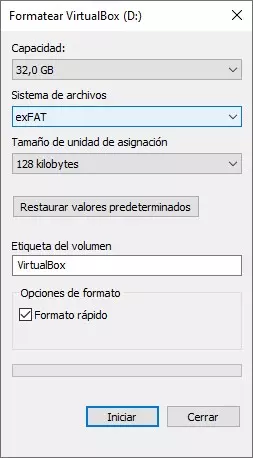
But, first of all, the first thing we are going to do is format the destination drive with the exFAT file system. This format is compatible with both older and more modern versions of Windows, a compatibility that we will not find in the NTFS format. If we use the FAT32 format, we will not be able to use images of files larger than 4GB, so it is also ruled out.
Once we have formatted the unit that we are going to use to create and use portable machines with the exFAT file system, we copy the folder where the portable version of VirtualBox has been created.
Next, from the external drive where we have copied the created directory, we run the Portable-VirtualBox application. Next, the main panel of the application will be displayed. For create a virtual machine (any machine that we create from this portable application will be portable, excuse the redundancy), we must click on New.
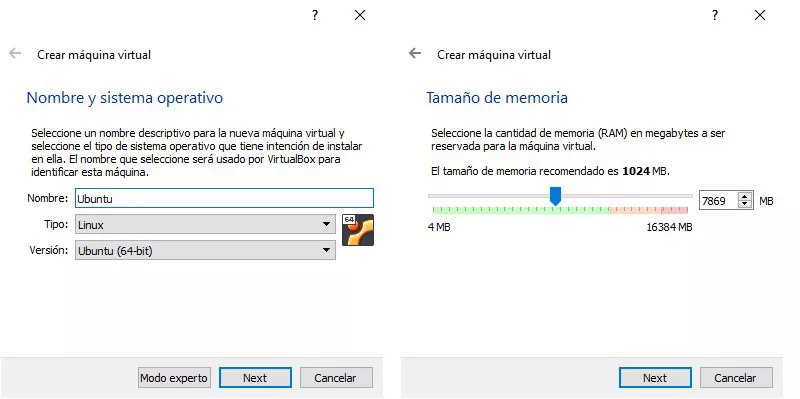
Next, we add the name with which we want to identify the virtual machine that we are going to create in the application. We select the type and version of the operating system (32 or 64 bits). Next, we select how much memory of the computer that we use we want to allocate to the virtual machine (we must take into account that other computers are going to use it so as not to select more than is strictly necessary and that it does not work on other computers with limited resources).
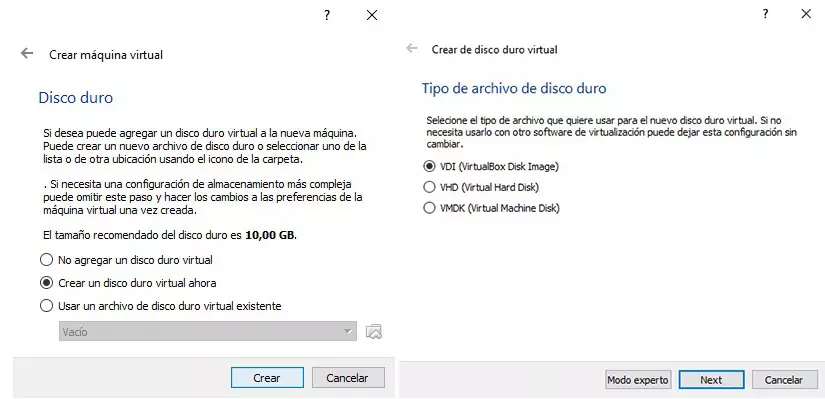
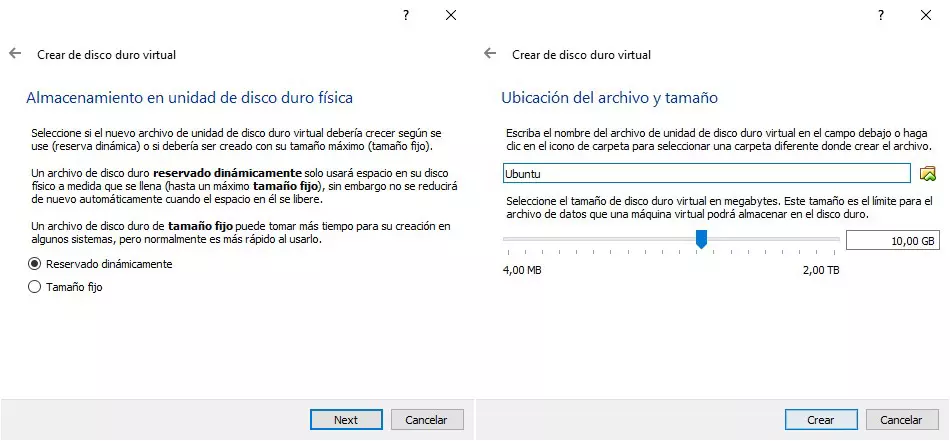
In the next step, in the Hard disk section, we must select the Create a virtual hard disk now option and in the Hard disk file type section, we will select VDI (VirtualBox Disk Image).
The last step before finalizing the creation of a virtual machine invites us to select whether to use a fixed size or whether the size will work dynamically, depending on your needs. Here, the best option is to select Dynamically Reserved. Finally, we select the location on our USB drive where we want to create the virtual machine along with the space we want to give it.
Once the process is finished, we must use the Windows or Ubuntu ISO that we want to install.
Advantages and disadvantages of using a portable virtual machine
Using a portable virtual machine instead of installing it on a computer, the first advantage it offers us is that if the use we want to give it is sporadic, we are not going to allocate an important part of our storage unit in a function that we are not going to use every day.
Another advantage it offers us is the versatility of being able to run any operating system on any computer, regardless of whether or not it is compatible with it. For example, through a virtual machine, we can make use of Windows 11 on non-compatible computers as it lacks both TPM 2.0 and secure boot.
The first disadvantage that we are going to find is the team power where we want to run it. When creating a virtual machine, we must select both the amount of memory that we want to allocate to the machine and the number of processors on the computer.
If the computer where we are going to use it is short of resources, the virtual machine will work just the same, however, the load time for practically anything we want to do will be eternal. To avoid this problem, it is recommended to always use as little memory as possible along with the fewest number of processors.
In this way, if we run the virtual machine on a device short on resources, it will not look for resources that it will never find, generating an unnecessary bottleneck.