The hottest element of a graphics card is its central processor or GPU, this, like all silicon-based semiconductors, is designed to operate without problems at temperatures below 100 degrees, however it is with 80 degrees that There are beginning to be problems due to overheating and that is why most graphics chips gradually lower their clock speed once they have reached certain temperatures and even their voltage.
However, a GPU may overheat due to the fact that its cooling system has stopped working properly and therefore is not releasing heat fast enough.
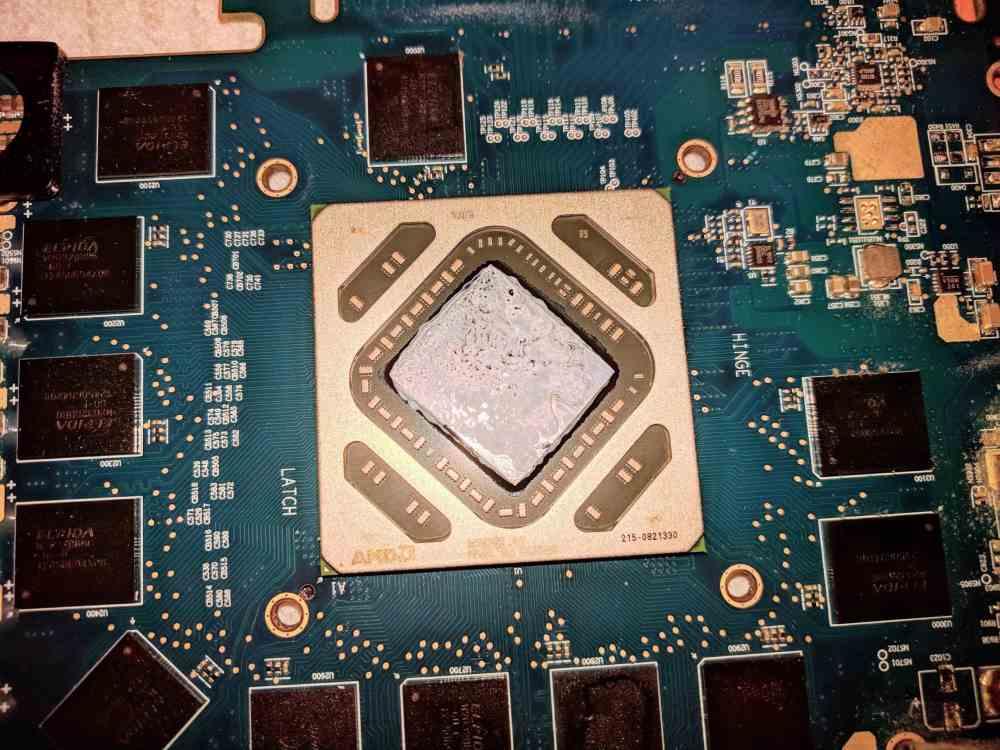
Dry or cracked thermal paste
As with processors, manufacturers put thermal paste on graphics cards to help dissipate the heat produced by the GPU. So, at a certain point, it will finish performing its function, so you will have to reapply the thermal paste every so often, for this you will have to disassemble the heatsink of the graphics card, which is not much of a secret to do. Of course, try to reassemble the entire graphics card cooling system correctly, things like a lame part, for example, can lead to subsequent operating problems.
Do not change the thermal paste for a liquid metal one, even if it manages to get some degree more, the manufacturers do not offer a guarantee due to the electrical transfer that is produced by static of the air from the fans to the heatsink and from this to the die as it is the conductive paste of electricity by its composition.
Fans don’t spin properly.
The function of the fans is double, on the one hand, to bring air at a lower temperature from the outside to maintain a stable operating temperature for the components of the graphics card. On the other hand, its job is to expel the hot air that has been dissipated by the heatsink to the outside.
Graphics card manufacturers often bring hardware that not only allows you to control the fan speed, but also adjust it as needed. The operation is simple, as the temperature emitted by the GPU rises, the number of revolutions per minute of the fans increases to accelerate air circulation. If suddenly a fan stops working then the lower temperature air does not enter, the higher temperature does not leave or both at the same time.
The problem of temperature measurement problems on which these applications are based usually take into account the data provided by the thermometer in or near the GPU, but do not take into account elements such as video RAM and power circuitry. for it. What do we recommend? Never turn off the fans and allow the fans to operate at 30% of their rotation speed in a temperature close to 35°C.
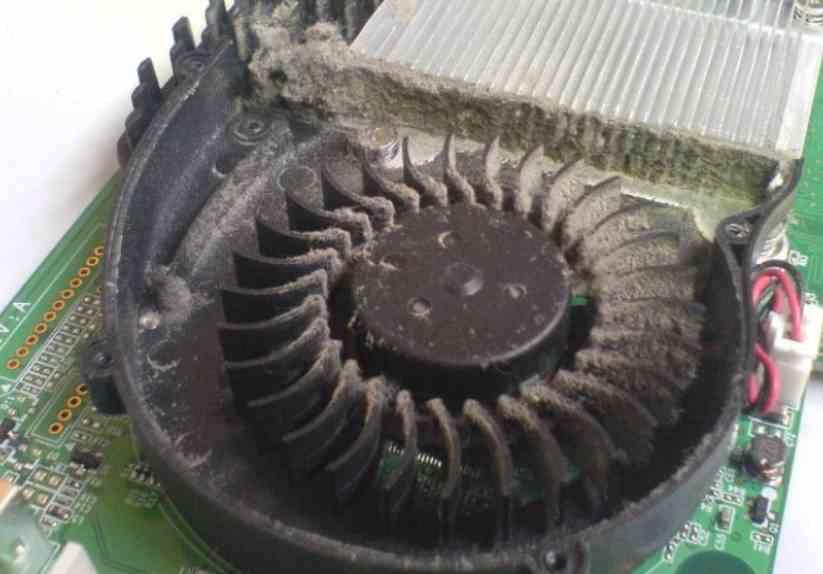
Fan cleaning and lubrication
We do not need to tell you that the periodic maintenance of the graphics card includes cleaning the fans, so when you disassemble the graphics card to replace the paste and the thermal pads, also make sure to clean the dust accumulated in fan blades, perhaps this is why they are not spinning as fast as expected. Also, that dust increases heat retention, being one of the reasons why your GPU overheats.
If we are handymen, we can disassemble the fan from its casing and lubricate it with some ceramic grease for bearings, Tamiya type, which has a molybdenum base and resists friction by displacing moisture and dust.
Thermal pads stiff and in poor condition
The types of memory used for graphics cards are the ones that consume the most of all those on the market, and the greater the amount of data transmitted, the more energy consumed and thus more heat. This being one of the reasons why a GPU overheats. So it’s important to keep the VRAM cool. Fortunately, the vast majority of graphics card manufacturers use dissipation and cooling systems that cover all the circuitry.
While in the GPU we have thermal paste to help with cooling, in the VRAM so-called thermal pads are usually used. The problem? There have been several models in which the thermal pads have been of poorer quality and, therefore, with poorer heat dissipation capacity. So from time to time you do not limit yourself to changing only the thermal paste of the GPU, but also the thermal pads of the VRAM.
We recommend this especially if you have bought a second-hand card today, as this could come from a mining farm. The reason? They overclock the VRAM to get more performance and that is why we recommend that as soon as you get the card you make sure to replace them.
Check the VRM pads
Another part in which the thermal pads are important is in the VRM and other elements in charge of distributing the energy to the different electronic systems of the graphics card, which are going to overheat when we overclock. In that case we give you the same advice as with the video memory, make sure to replace the thermal pads from time to time and that they make contact with the graphics card cooling system.
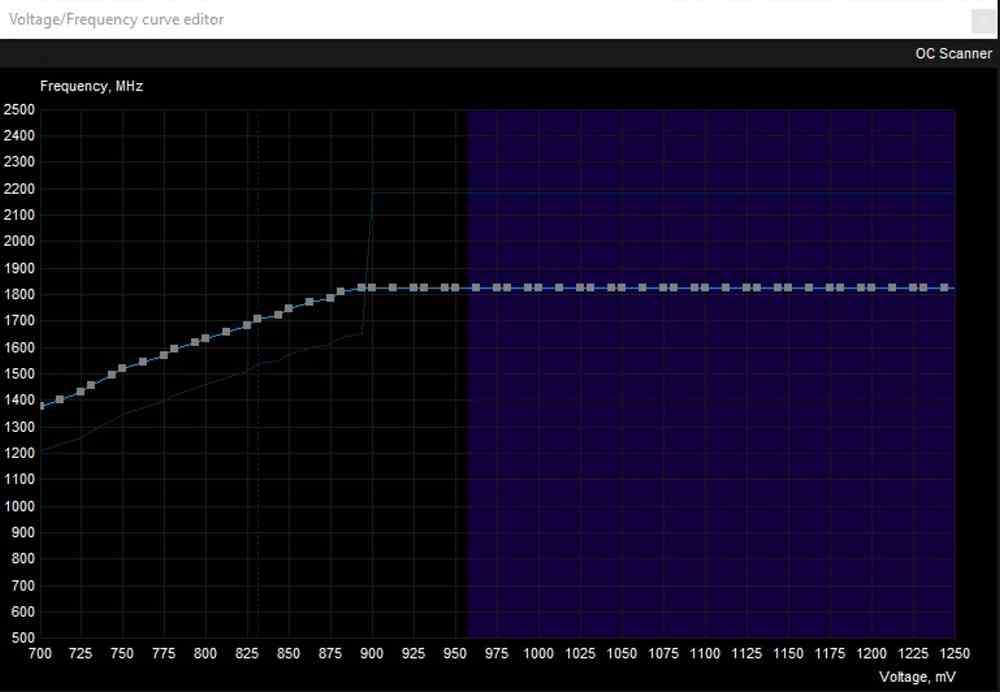
undervolting
A graphics card with its GPU running at 2 GHz and a voltage of 1.2 V will work in the same way as the same model at the same speed but at 1 V consumption. The advantage? It will consume less, and with it it will generate less heat. So if you can safely undervolt your graphics card just do it, as it will give it a longer lifespan.
The disadvantage of undervolting is that the peak or Boost speeds that it will be able to reach will be much lower, but in return you will see how the GPU overheats less at normal use speeds. Of course, make sure you use tools from the graphics card manufacturer designed for it and do not go outside the specified voltages. The trick with undervolting is to get the sweet spot between the voltage and the right clock speed.